SEO Image Optimization Guide: How to Rank at the Top of Google Images SERPs

We've created a detailed guide on image optimization for SEO based on a recent presentation by Yaroslav Beshta — Promova's Senior SEO Specialist. It covers all tips and tricks on optimizing your images to improve SERPs and get traffic from Google Images.
About the Speaker

Yaroslav Beshta is a Senior SEO Specialist at Promova company. He started his website promotion career in gray niches but later transitioned to white-hat SEO. He has since worked on multiple E-commerce projects targeting the markets of Ukraine, the USA, and the UK.
He also hosts a “Shozashum" ("What's that noice" in Ukrainian) podcast, where he shares his experience in SEO and marketing.
So, let's dive into how images improve SEO, how to create and optimize SEO images, and how to easily drive traffic from them that converts into revenue.
Let's hear more from Yaroslav👇
Technical Images vs. SEO Images
Image optimization for SEO is a set of actions to improve a website's visibility for search engines. It positively impacts page loading speed, user experience, conversions, and traffic and is crucial to SEO promotion.
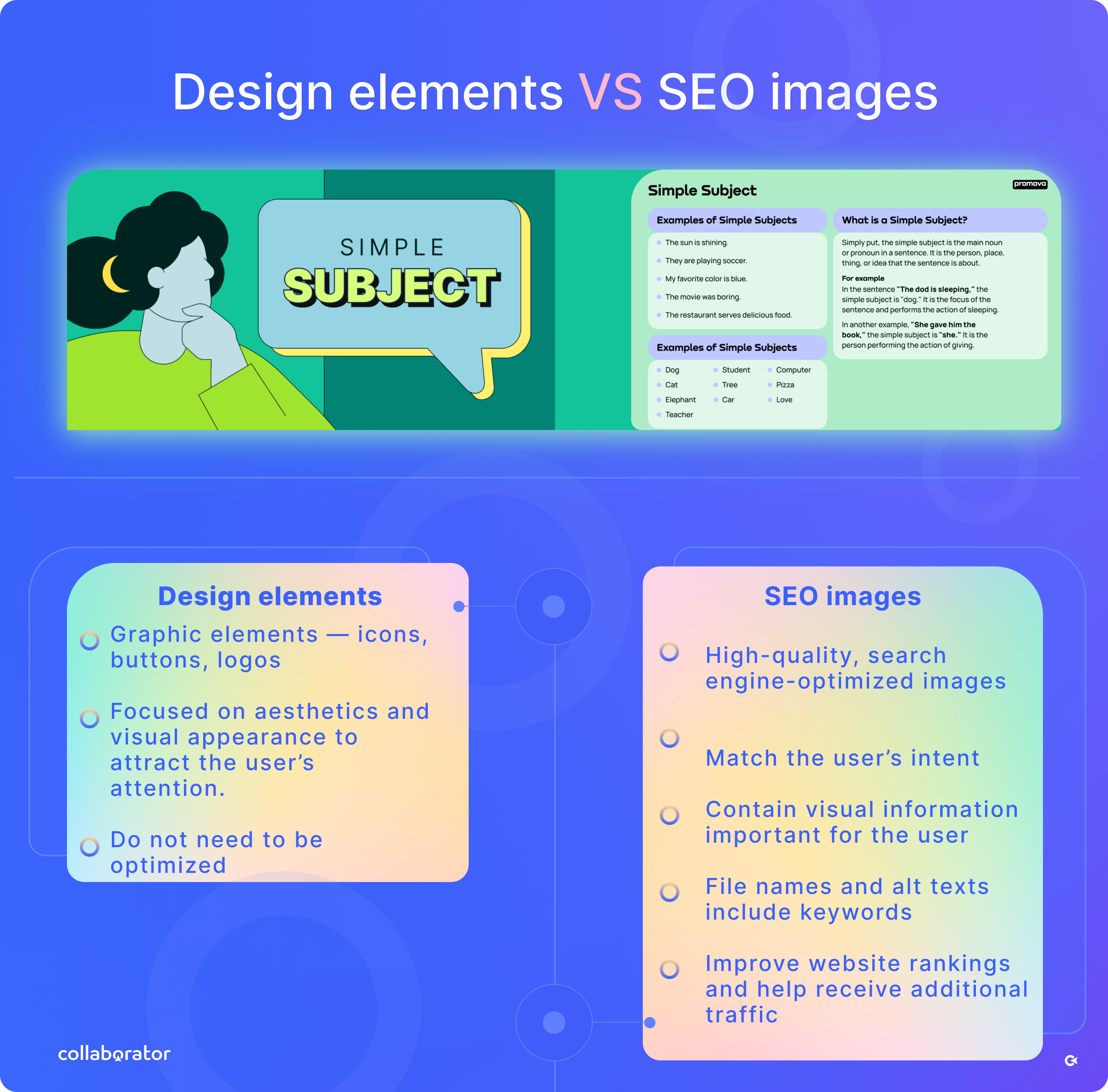
First and foremost, not all images on your website can generate traffic. You do not need to input alt, titles, and keywords for your regular website icons or other design elements.
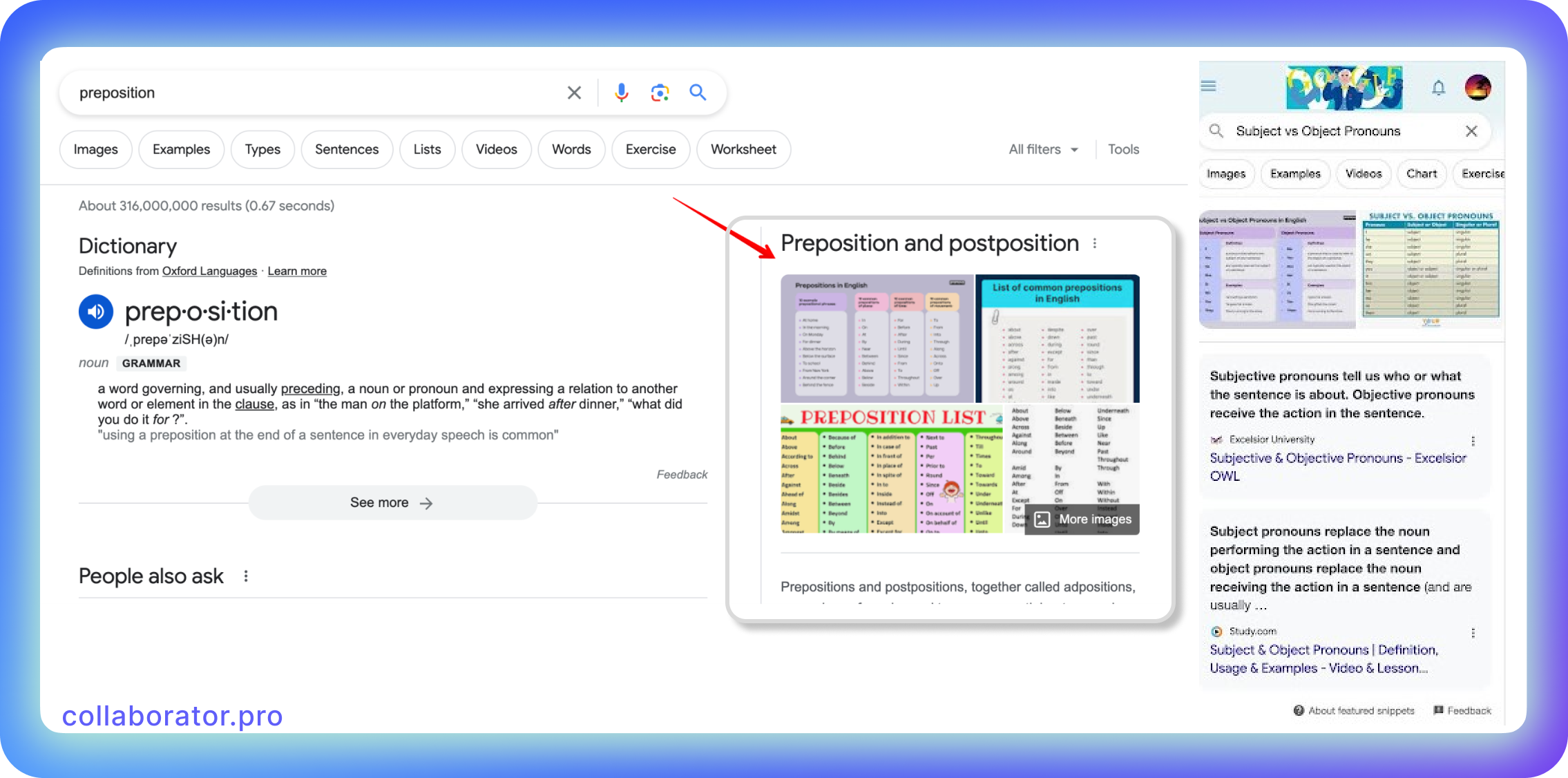
Google is good at distinguishing different types of images to provide the user with relevant visual content. SEO-friendly images that include explanations or examples on the specific topic are the most useful to the user, providing him with the solution, so Google gives preference to them and makes them appear higher in search results.
On the left is an image that doesn't provide any helpful info to the user, and on the right is an image that Google will consider helpful
So, what do you do with non-SEO images?
- You can add design elements with CSS styles. If you don't want Google to spend its crawling budget on website design elements, we recommend using CSS styles; this way, Google will not index the image. It will only 'notice' your images if you use tags <img> and <picture>.
- Only try to optimize images if they're relevant to your intent. Just accept it 🙂 If your competitors invest in SEO images, do not try to compete with them using non-optimized images: they won't help you rank higher, as Google will not see them as helpful to its users.
How to Get Google Image Traffic?

An infographic on key methods of image optimization for SEO
You must follow these simple image optimization rules for SEO to generate traffic.
- Create unique images. Use Canva, Photoshop, or any other editor to create unique images. Stock images can also work, but you must remember that others can use them, too. If you didn't get rid of IPTC and metadata, you would help the original website rank higher than yours.
- Match the intent. Google prefers images that are relevant to the user's search intent.
- Create short alt & title texts. Do not use the exact words word-for-word, but ensure they all match the same intent. You do not necessarily have to use as many keywords as possible. Alt text is supposed to explain the image's content using 100-150 symbols max.
- Create correct image URLs. Image URLs should include keywords. This, as well as the alt texts and title, will help Google understand what is happening in the image.
To better understand Google's needs for SEO images, check out Google's recommendation guide.
Image Size and Weight
What should be an image weight? It's a common mistake to think that large images affect SEO and their weight shouldn't be higher than 100 kB, all thanks to Screaming Frog's mention of this number.
Image size plays a crucial role in the page loading speed, but there isn't a specific limit. Of course, it's better to avoid 20 MB pictures as it will be as slow as Internet Explorer🙂 And don’t forget to include keywords in image file names!
If you’re looking for an SEO image optimizer online, there are various free image SEO tools available to streamline this process. Finding an image SEO tool free of charge can be a practical approach to automating some of these tasks.
You can use this table of standard SEO image sizes as your ultimate guide:
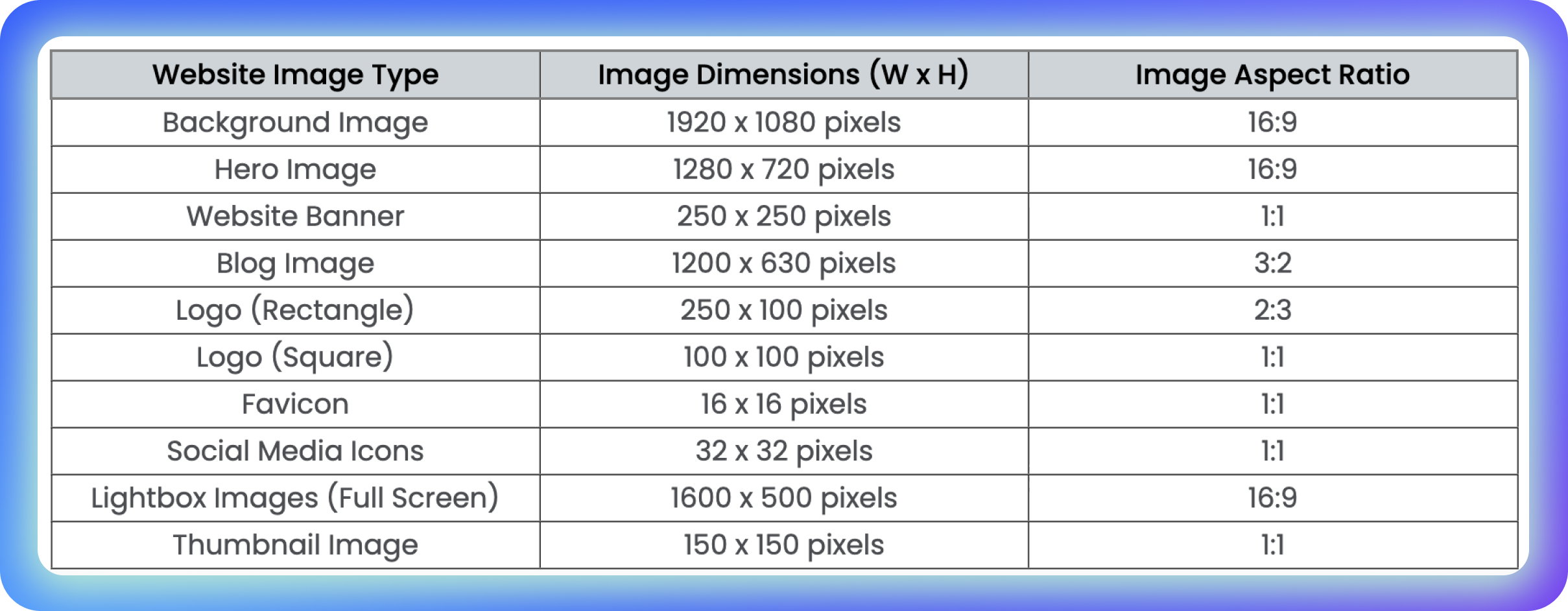
A helpful comparison table of website image types and their dimensions. Source
Google loves high-quality SEO images, so to rank higher in Google Images SERPs, use larger formats. Use the src attribute to reduce file size and deliver the largest image file, even in Full HD. It's especially helpful for online shops, as it will help them stand out from their competition.
To create a good user experience, you should also use:
- Image compression. You can use SEO image optimization software such as Tiny-img.com, Tinypng.com, Compressor.io, and Imagemagick.
- Webp image format. This file type will ensure the optimal balance between the image size and quality.
- Adaptive images. This way, the user will see a small image loading fast, and Google will see a large, high-quality image. You can do so in two ways: tag <img> + src-set array and tag <picture>.
Using src-set
<img
srcset="maine-coon-nap-320w.jpg 320w, maine-coon-nap-480w.jpg 480w, maine-coon-nap-800w.jpg 800w"
sizes="(max-width: 320px) 280px, (max-width: 480px) 440px, 800px"
src="maine-coon-nap-800w.jpg"
alt="A watercolor illustration of a maine coon napping leisurely in front of a fireplace">
Using <picture> tag
<picture>
<source type="image/svg+xml" srcset="pyramid.svg">
<source type="image/webp" srcset="pyramid.webp">
<img src="pyramid.png" alt="An 1800s oil painting of The Great Pyramid">
</picture>
Ensure you're providing the search bot with a src link to the image; otherwise, it will not exist for the bot.
You can check out the Responsive Images guide here.
Microdata ImageObject and HTML Сode
You won't be able to outsmart Google, so it's better to play by its official rules 🙂
Remember to conduct competitors' research and see if they're using ImageObject microdata. Optimize your images and include all necessary attributes, and you'll be golden.
Use <figure> and <figcaption> tags to group images with captions for better page structure and semantics:
<figure>
<img src="path-to-image.jpg" alt="Image Description">
<figcaption>Caption:Further Image Description</figcaption>
</figure>
IPTC Metadata: Content Protection
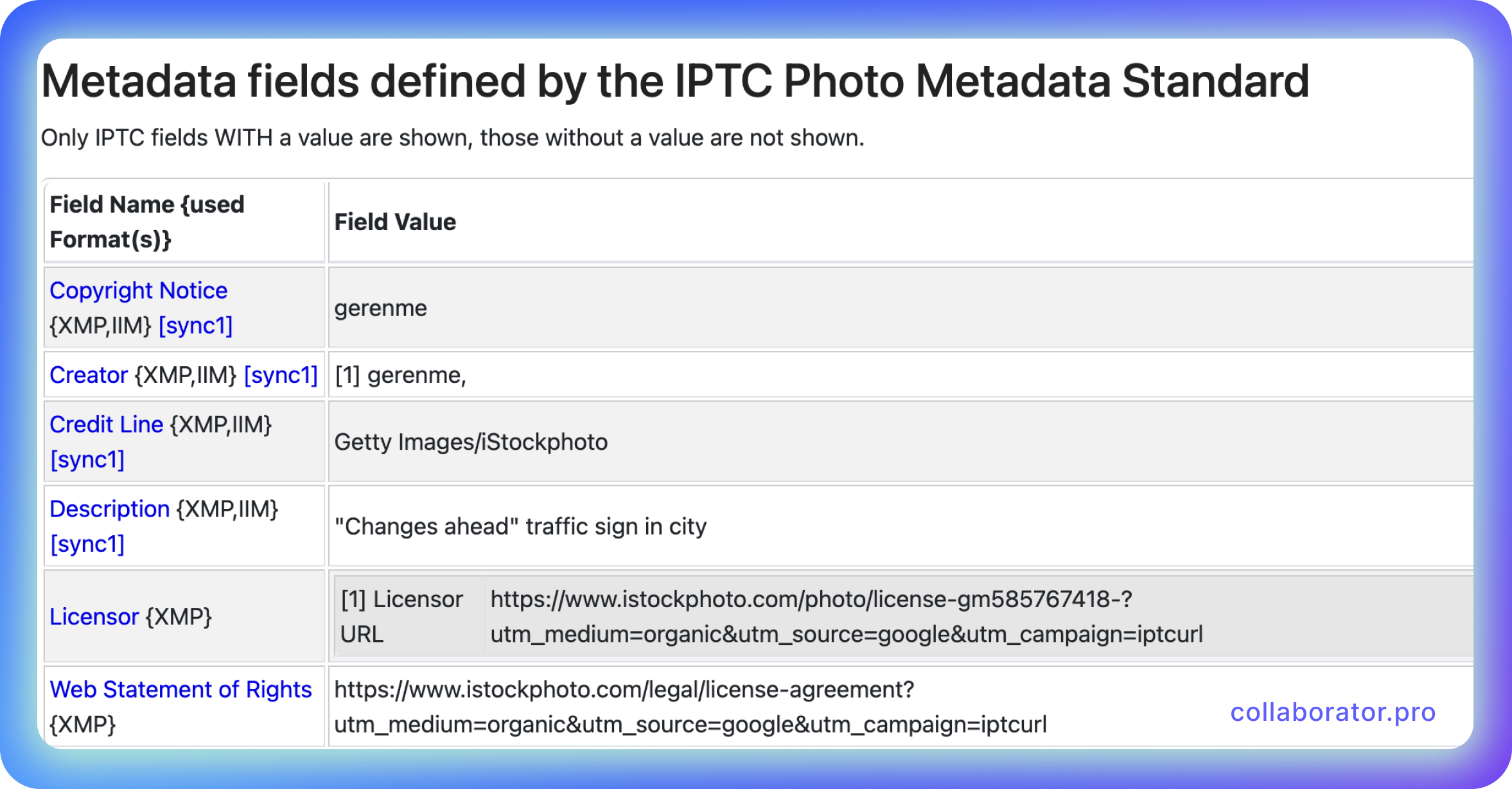
Not everyone actively uses IPTC metadata, but it's still significant in terms of copyright protection and content identification. By filling out this data, you can prove that you are the original copyright owner in case your content is stolen. You can add IPTC metadata directly in Photoshop or while uploading the image to the server.
Here are the seven critical fields for IPTC metadata:
- Title: short description or name.
- Description: a detailed description of the content.
- Keywords: the words or phrases that best describe the image.
- Author: the name of the original image creator.
- Copyright notice: information about the original copyright owner.
- Date of creation: it usually pulls up automatically.
- Location: the data about the geographical location where the image was created (it also pulls up automatically).
One of the top IStock creators is filling out metadata, resulting in 40-50 million traffic from images.
Sitemap.xml for Images
This one's easy: pack all your SEO images in one map and submit it to your console or robots — whatever's more convenient for you. Google will see them all. Make sure to include only the images that can generate traffic.
Generally, using Sitemap.xml for your images is a great way to improve your website's visibility and SERPs rankings.
Dangerous Lazy Load
You may often hear about Lazy Load's usefulness, which helps your image load faster. Indeed, it works this way. However, it's easy to confuse the two types of Lazy Load — browser-based and standard, where a placeholder is used (meaning that the user will see a loading animation). The latter can lead to a lot of trouble.
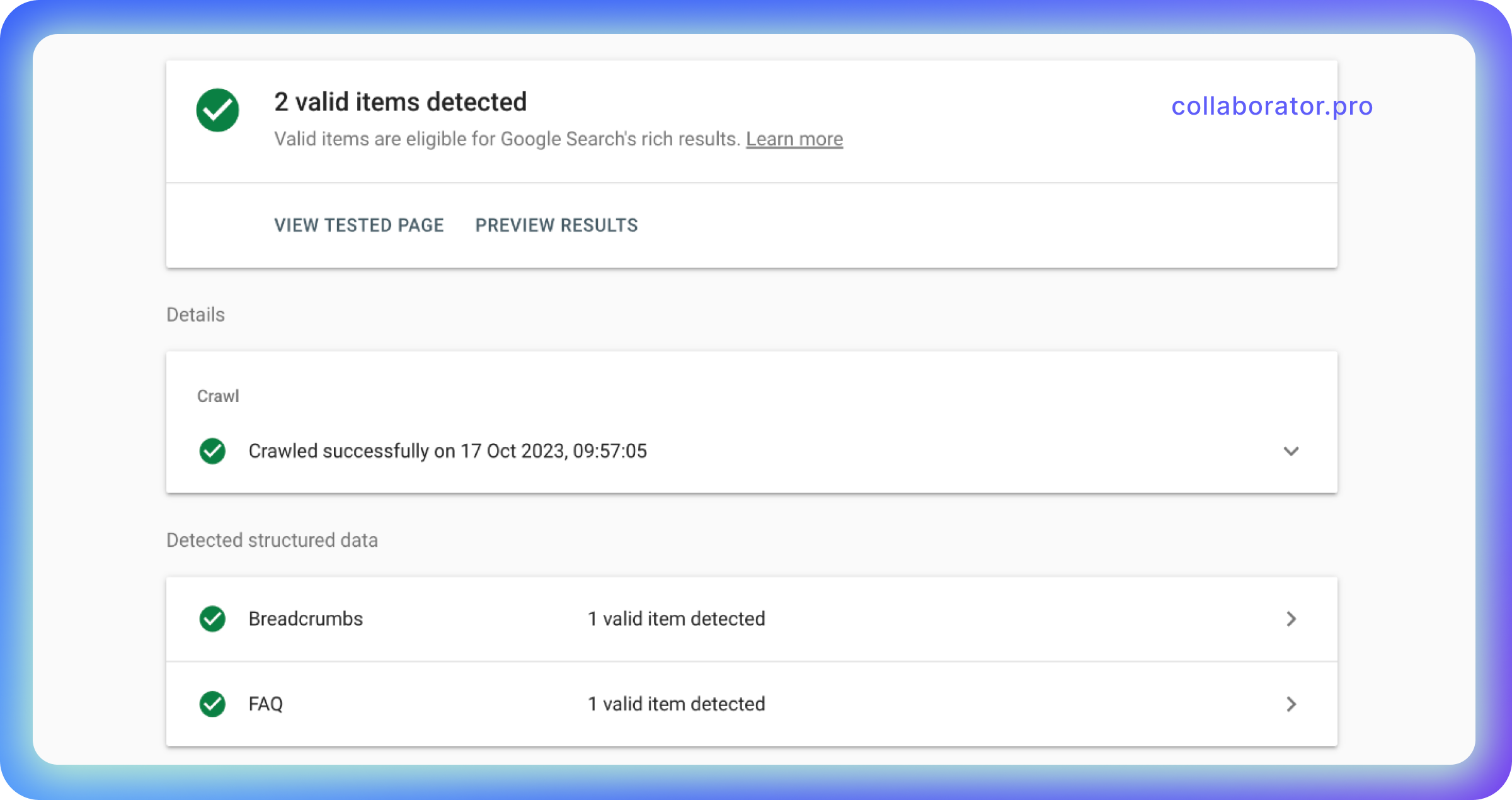
An excellent example of this common mistake we've found in an online store in the thermal mugs category:
With the help of the Rich Snippets Tool, you can see that the first screen displays the images, and the next doesn't. This happens precisely because Lazy Load is used with a placeholder.
Remember that the Google bot does not scroll your webpage—he cannot do that. He's just loading the image. So, if you're using a placeholder for Lazy Load, the bot will only get the first four images and won't see any other ones. As a result, you're losing to your competitors who set up the browser-based Lazy Load.
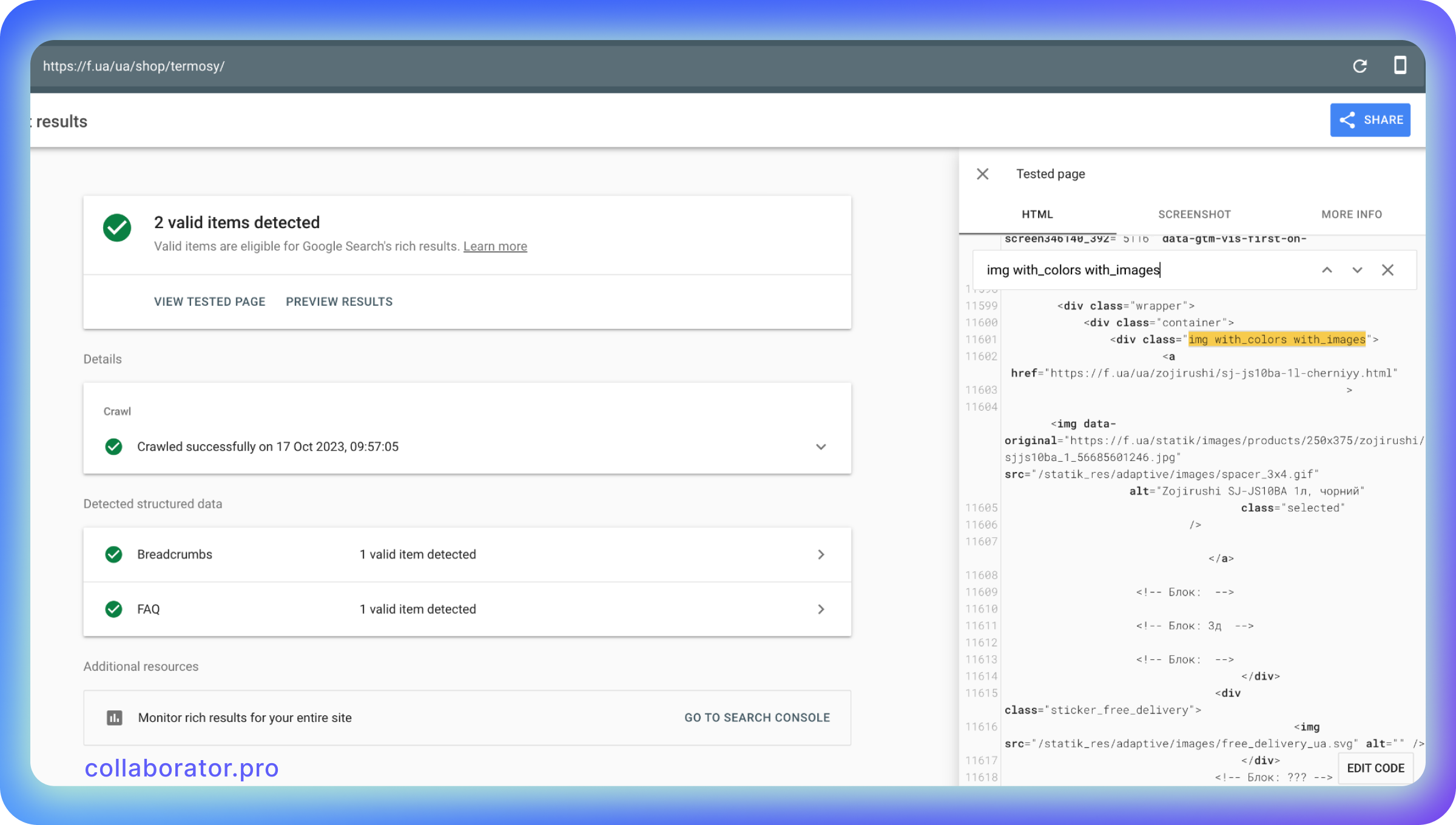
Our recommendation is to avoid the standard Lazy Load. It's way better to use adaptive images. You can check which Lazy Load your website is using with Rich Snippets Tools:
You can see an error in this code: the website uses a static GIF image here, meaning the Google bot will see it instead of the images.
You can read more about this problem in this Case Study.
Why Do I Bother?
Why should you invest your time and resources in images? First of all, for revenue, as traffic leads to conversions.
For an SEO image optimization example, we will take a look at our website (Promova), which ranks approximately in the top 20 by the "Simple Subject" query. However, our image appears on the first screen. Here, while using two top keywords as an example, the website ranks in the first engine search positions, as the images completely match the user’s intent:
The articles don't rank at the top but still generate constant traffic because they appear higher in Google Images.
If you create a quality image, you can rank at the top without buying backlinks because you have outstanding, SEO-optimized images.
Image Optimization Results
We'll tell you about two real cases from Yaroslav's experience. In the first case, they started from scratch without having any SEO images. They created a roadmap and thought through which images they needed and what they needed to look like. They also planned and implemented the strategy, which the graphic designers successfully utilized. The whole process took six months, and here are the results:
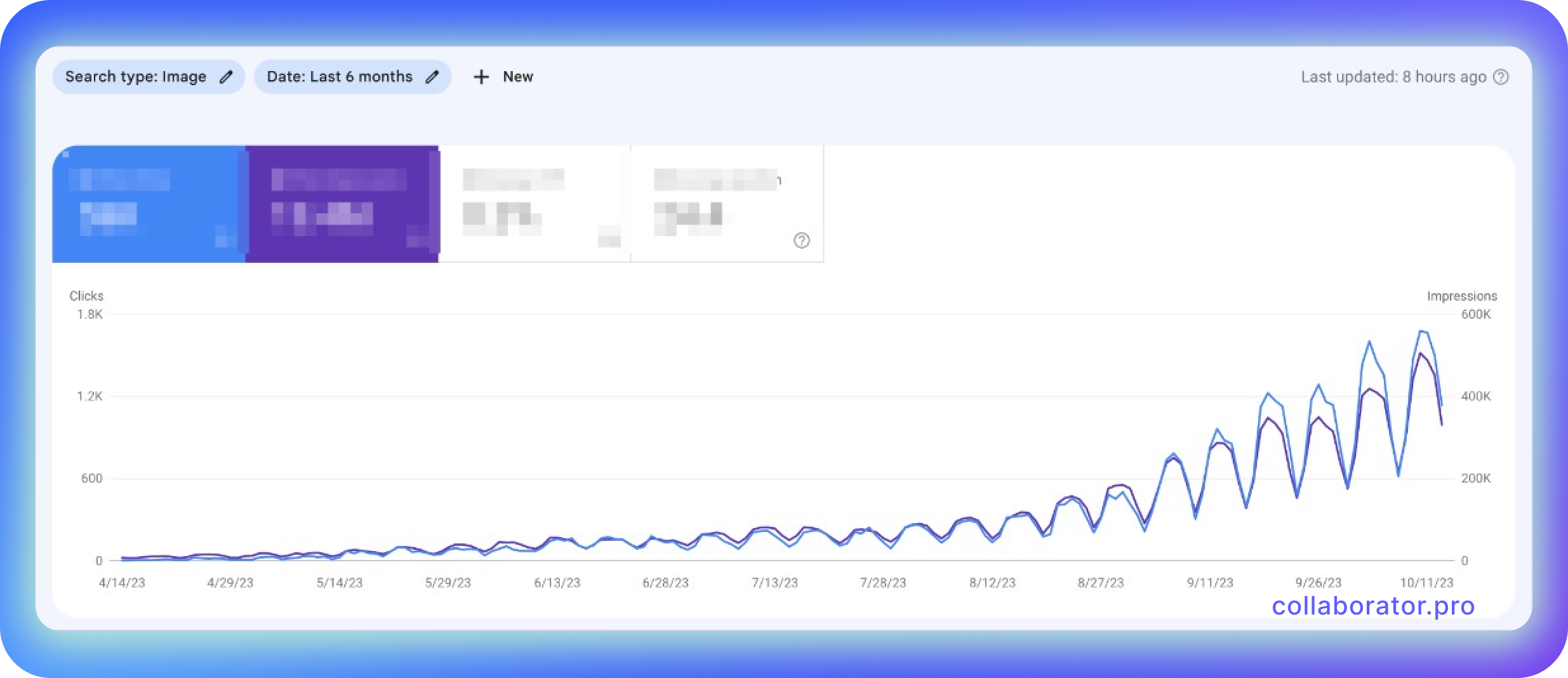
This process helped generate over 2000 image clicks daily.
This example tells about implementing SEO images at the beginning of the process. When they first released the website, they quickly realized they could withstand the competition simply by creating original high-quality content that ranks at the top. This is why they focused on investing resources in content creation, which had its benefits.
Here's an example of the website that made adjustments to existing images:
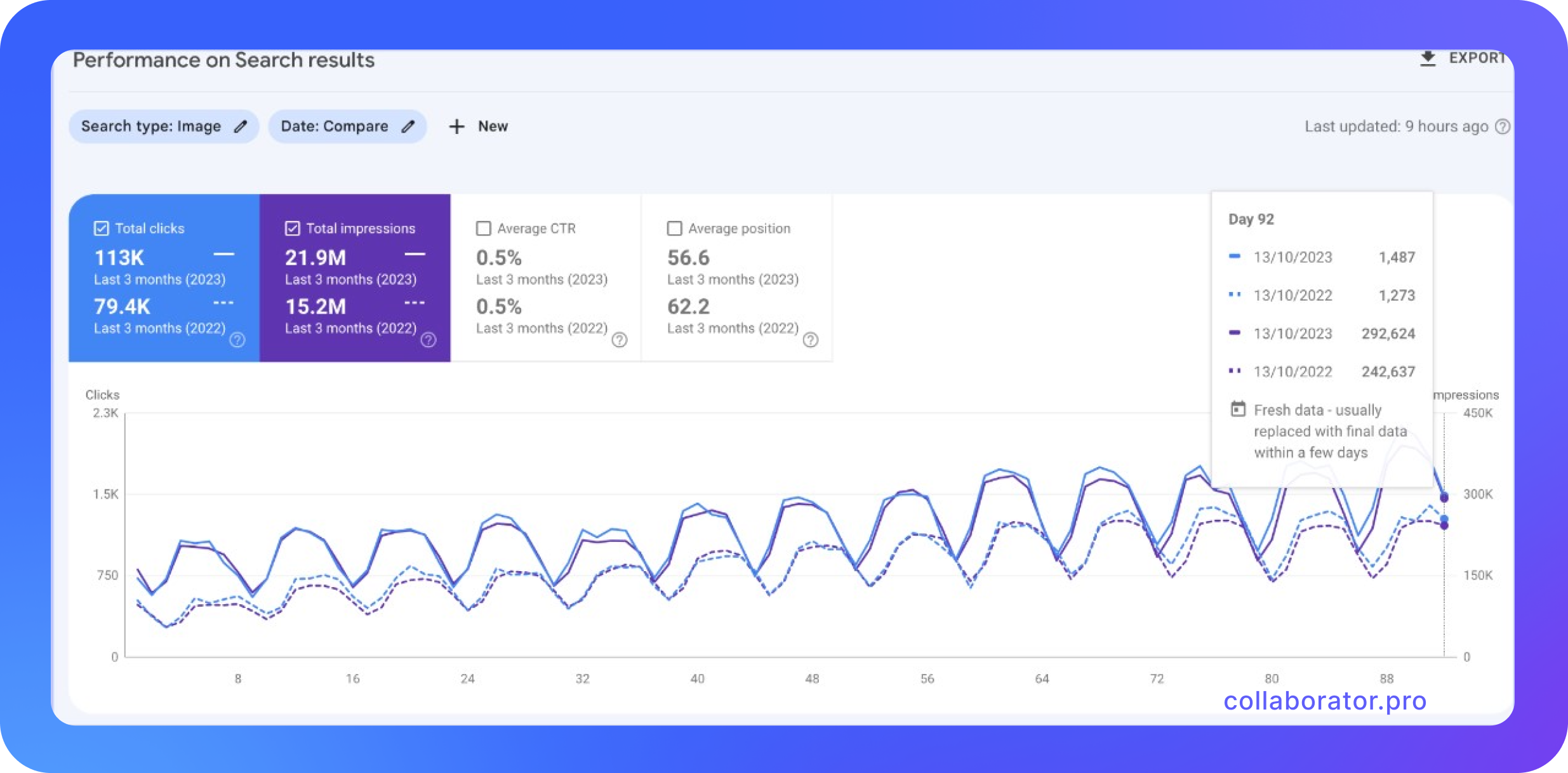
In this case, the problem was that the links did not get into the source, leading to the bot not seeing the images.
After fixing it and setting up the correct alt and title tags and layout, they still received great results: 80 thousand clicks at first, eventually raising to 120 thousand.
AI Image Generation
AI image generation is an excellent tool to use if you want to receive image traffic but need a design team. Check out this detailed step-by-step video guide to help you generate SEO-optimized images with Canva and AI.
For just $7, you can get Canva premium features that allow you to generate your images in bulk. For instance, you can create prompts and generate the texts for future images in Google Sheets or Excel. Then, using the bulk mode, all data can be easily imported and instantly generated up to 200 images.
The process is intuitive and easy to understand: pick a template, select the fields needed for content input, and generate. All images are easy to edit, too. All that's left is to upload them to the website while adhering to the SEO images optimization guide. You can also read more about implementing AI for SEO in one of our previous articles.
Q&A
Do you have to redirect old image URLs if you transfer to CDN?
Generally, it's recommended to use CDN only for large enterprise projects. It's optional for smaller websites as the costs are not justified.
Regarding the redirect, there are cases when URL changes lead to a drop in rankings. We wouldn't recommend doing this, as there's already an accumulated effect, and Google will need some time to re-crawl everything. As a result, it can work out, but you have to consider all the pros and cons and decide if you're ready to pay this price.
What should you consider when creating infographics for the articles?
I have a classic SEO approach: if there's an intent, I'm looking at Google search results and the snippets and analyzing the competitors and their graphics. Depending on which content I have, I'm creating my plan according to the competitors.
However, this is a question for both SEO specialists and designers. My rule is to make it better than my competitors. It's also essential to keep your infographics and images manageable, as they must be easily readable and understandable.
If my website has many images, should I go back to them and fill out the correct alt and title tags? Will the search engine see these changes?
First of all, you need to understand what niche your website is in and what the traffic situation is like. Go over all the recommendations above and analyze what you've already implemented. Make sure that you are using SEO images. If you are, and they can generate traffic, I would recommend doing that, as that's your future revenue.
What's the role of the image title when compared to alt attributes?
It's hard to say. As with the audit, you often need to figure out what exactly got you the best result. I usually consider the result.
I would add keywords to URLs and alt texts but optimize them accordingly.
Can I use English alt text if I’m promoting a website in another language?
You can, but what for?🙂 If the website is in another language, then your market is different, so how are you supposed to be found by English keywords? You will not rank higher in the US either, as their market has its own players with already strong domains. So it doesn't make sense. Create your alt texts according to the market you're targeting.
Which WordPress plugins do you use for image optimization?
I do work with WordPress now, but I do remember that its latest version had adaptive images. I didn't even set up an additional plugin, so I can't recommend anything specific.
How does it affect my traffic if I already have all the information on the image, meaning that the user doesn't necessarily go to my website?
Of course, it's sad that the user does not visit the website. In this case, you have to look at the bigger picture and not just at search engine optimization, as this includes behavioral factors.
In this case, we usually add our logo to all images and hope that the users will remember the brand this way, leading them to recognize it in the future.
Is there a reason to use image hosting services such as Imgur? Or is it better to upload all your images directly to your website?
If you're using image hostings, you're only helping with their link building. If you want to generate traffic, the image should have your domain. If you're using other's content, its owners will be thankful for generating traffic for them, but you will not benefit from it.
Will slight changes in the image, such as mirroring, cropping, and editing, help, or is it not even worth a try?
If you steal content from someone with good lawyers, you can receive DMCA complaints. But if you photoshopped it a bit, they might not be able to find it, as it will also alter the metadata. Change your alt, title, and URL—and it's even harder to find. But it depends on your end goal: it won't end well if you want to copy from your competitors.
Is it necessary to create a sitemap for images?
It's not necessary. It's just what Google recommends to make finding your images easier. If you see that the Google bot sees the source (you can see it in Rich Snippets Tool or GSC), you do not have to do it.
How do we ensure the Google bot receives the image in src?
There are some different options:
- Mobile Friendly tool, which emulates the Google bot;
- Rich Snippets Tool;
- GSC, if this is your website.
Should I delete Exif data before uploading the image to the website?
Exif data is still not really common, so I didn't mention it. If you're using images uploaded to image hosting sites, it will help you reduce their weight a little bit. If you have a lot of graphic elements and you're counting every megabyte, you can delete them—it will help you reduce memory usage.
If you buy your graphics from IStock or Freepik, carefully read the license. If I'm not mistaken, sometimes you can get rid of Exif data and replace it with yours, but you have to read the documentation as it's not included in the agreement.
What happens with image optimization on Pinterest? If I use Pinterest images with my unique H1 in the article, will my website appear in SERPs if I use a Pinterest image?
I don't specialize in Pinterest optimization. We have Pinterest, but we post visuals that are different from those we use for your blog or website. If it's specifically an SEO image, we use it only for the website, but if we have a lot of visuals, we can upload some of them to Pinterest.
Should I protect unique images? How do I do it correctly? Or can they be stolen either way? Is it possible for Google to scan the stolen image before the original image?
It depends on your niche. Regarding how to do it — there are DMCA complaints. If you see that your image was stolen, you can submit a complaint, and it will be taken off Google. But nobody will be able to delete it from the website. This is more of a legal aspect.
You can write out the rules for using your images, but let's be honest: Not many people will adhere to them. Western markets are using footprints.
What's the record number of clicks you had from one image?
It's hard to say. The impressions can be wild. In 28 days, a particular keyword has up to half a million impressions but only 2-3 thousand clicks.
The Collaborator's Team is thankful to Yaroslav for his expert presentation and practical image optimization tips. We wish him and our readers top SERP rankings and a significant traffic increase. Now that you know the best image SEO practices, promoting your website online is even easier!