Accuracy of Ahrefs, Semrush, and Similarweb: Which SEO Tool Is Best for Traffic Analysis?

Can you really trust the numbers? Let’s break it down.
Numbers are supposed to be the ultimate truth, right? Every time SEO analysts present reports, clients raise an eyebrow when the data from different sources just doesn’t match.
So, why do popular SEO tools give conflicting metrics? More importantly, which ones should you rely on when making those big, strategic moves? Let’s dive in and separate fact from fluff!
SEO Tools Accuracy Case Study: The Goal & Methods

When SEO clients start asking those inconvenient (but totally genius) questions, Promodo's marketing mavens don't just take notes — they launch a full-scale digital investigation. Vladyslav Trishkin and his data-detective squad zeroed in on three mission-critical objectives:
- Investigate the error margin of popular SEO tools: Semrush vs Similarweb vs Ahrefs.
- Gather evidence-based data and analytical insights from a sample of websites to identify patterns in discrepancies.
- Draw conclusions that will help SEO specialists better explain results to clients and build strategies based on real data.
To achieve the most objective and comprehensive results, the analysis was based on a sample of 184 websites from different regions, niches, and with varying traffic volumes:
The data for the first half of 2024 was analyzed from the following sources:
- Google Search Console — used as a reference for actual metrics.
- Ahrefs, Similarweb, and Semrush — used to compare the "synthetic" data they calculate.
The research examined the error margins of various SEO services when compared to Google Search Console (GSC) data. The study revealed interesting patterns in how different tools measure and report metrics.
They discovered that some tools consistently overestimate or underestimate certain metrics, providing valuable insights into their reliability.These results offer SEO specialists a clearer understanding of their analytical tools' limitations.
The key takeaway? Not all SEO tools are equally precise, and understanding their individual characteristics can significantly improve your digital marketing approach.
Traffic Calculation in Semrush, Similarweb, and Ahrefs
Each SEO service has its own unique traffic estimation system, which impacts data accuracy. Next, we will explore how Semrush, Similarweb, and Ahrefs estimate website traffic, examining their methodologies, strengths, and weaknesses.
How Semrush Calculates Traffic Data
Semrush uses petabytes of clickstream data sourced from various third-party providers, though the exact sources are not disclosed.
For organic traffic, Semrush employs a predictive model that analyzes keyword rankings. The model multiplies the CTR (click-through rate) by the search volume for specific queries. This method provides fairly accurate estimates for medium and large websites. However, for sites with low traffic (<5,000 clicks per month), accuracy drops significantly.
It’s important to note that Semrush delivers estimated data rather than actual metrics, which inherently introduces a margin of error.
How Similarweb Calculates Traffic Data
Similarweb gathers data from four main sources:
- Direct measurements (data from websites that provide access to their internal tracking systems).
- User behavior data via the Contributory Network.
- Digital signals from partner organizations.
- Public Data Extraction, an algorithmic tool that collects data from a vast number of websites.
A key advantage of Similarweb is its comprehensive insights across all traffic channels, including organic, PPC, and referral. It offers detailed reports in a user-friendly format, with options for competitor comparison.
After a global tracking system update in late July 2024, accuracy improved. New parameters were introduced to account for not only actual changes but also seasonal traffic fluctuations, along with enhanced insights into mobile traffic.
However, accuracy for websites with low traffic remains limited, as the service relies heavily on large data volumes from its various sources.
How Ahrefs Calculates Traffic Data
Ahrefs bases its traffic estimation on search queries, their volume (demand), and its own custom CTR calculations. The service provides fairly accurate data but primarily for websites with stable rankings. When SERP positions change rapidly and Ahrefs’ crawler has not yet updated the data, the traffic estimates can become outdated.
Additionally, Ahrefs does not offer a cumulative monthly traffic estimate, which can complicate long-term analysis.
In simple terms: Ahrefs estimates daily traffic based on current rankings, CTR, and search queries, projecting an approximate monthly figure. This approach introduces several potential points of error, given the many variables involved.
Research Results on the Accuracy of SEO Services: Average Margin of Error
After analyzing each service and processing massive datasets, Vladyslav and the team calculated the average error percentage.
Let’s break it down by each SEO tool.
Semrush demonstrated an average error rate of 61.58%, with a tendency to overestimate traffic (in 112 out of 184 websites).
Certain anomalies were observed: in some cases, Semrush estimated traffic at 130,000, while the actual volume was 50,000.
At the same time, there were instances of minimal deviations, close to actual values.
In Similarweb, the error rate is lower at 56.95%. The improved results are likely due to the system update in July 2024. Prior to this update, the error margin was significantly higher, but since then, the estimates have become closer to actual values, although the service still tends to overestimate data.
Similarweb more frequently than Semrush and Ahrefs demonstrated results with minimal error, closely aligned with actual traffic. Anomalies exceeding 100% were still present, but due to the overall trend of improvement, it is expected that accuracy will continue to increase.
Ahrefs ranked first in terms of accuracy, with the best error margin of 48.63%. In most cases, this service showed metrics closer to the real traffic, but with a tendency to underestimate traffic. Anomalous errors were practically nonexistent, though there were also few instances with minimal deviations.
The average error margin for the tools studied is about 50%. However, during the investigation into the accuracy of SEO services, anomalous cases were found where results significantly differed from actual values. These discrepancies were not dependent on the niche or size of the websites, indicating the limitations of each service’s methodology.
These findings drive home one key point: no single tool has all the answers. To dodge major errors, you’ve got to cross-check data. Remember, accuracy isn’t just a numbers game. It’s a moving target influenced by fluctuating CTRs, shifting rankings, and how fast each platform updates its intel.
How to Calculate Traffic Yourself: A Step-by-Step Guide
You can perform the calculations manually. Of course, they will also have some margin of error, but the key advantage of this method is that you won't need specialized services.
To calculate traffic, you need the following data:
- A complete semantic core (keyword set)
- CTR for the top 10 search results
- Position and frequency data (search volume and keyword rankings)
To begin, collect all relevant queries — high, medium, and low-volume keywords — for the page, category, or site you want to analyze. The position and frequency data will allow you to assess the site's visibility for the selected keywords.
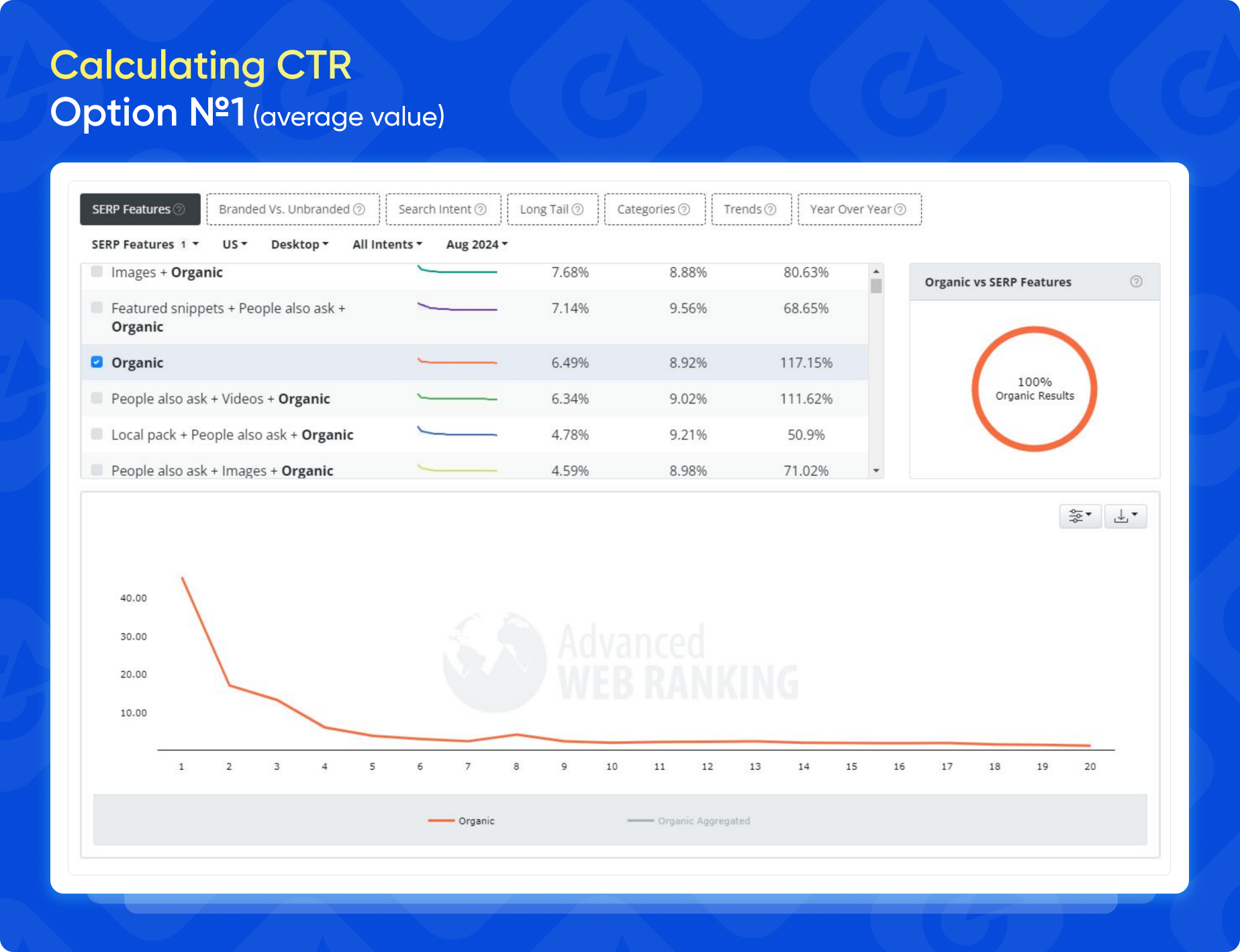
To determine CTR, the easiest method is to use average metrics from services like Advanced Web Ranking. This tool shows current trends for CTR, but note that the error margin will be large due to variations in search results depending on niches, regions, and the presence of different blocks in the SERP (such as People Also Ask, Local Pack, Images, and expanded snippets).
Another option is to gather data from Google Search Console. Filter queries by category, excluding branded terms. Then, calculate the average CTR for each position (ideally from 1 to 10). This will provide data based on your site’s historical performance.
Next, we move on to the traffic calculation:
- Create a table with the following data:
- Query
- Search Volume (Frequency)
- Current Position
- CTR for this position
- Use this formula for calculation:
Traffic=(Frequency × CTR) ÷ 100 - Sum the results for all keywords to get the estimated total monthly traffic volume.
By using this method, you will be able to estimate the potential traffic based on the search volume, position, and CTR for each query.
This method is effective for analyzing individual pages or categories, but for large-scale projects (such as analyzing an entire website or a competitor), it can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Key Takeaways
Don’t expect external tools to dish out flawless numbers — they’re good, but not crystal balls. Organic traffic estimates come with a built-in margin of error since real-time tracking of every variable just isn’t possible. So, when crafting your SEO strategy or stalking competitors, remember: it’s all educated guesses, not gospel.
Want better accuracy? Roll up your sleeves and crunch the numbers yourself. A little DIY can reveal site-specific insights that no tool can match.
Q&A
Why do Ahrefs' "Linked Websites" metrics not match the data from their free link checker tool?
This question should be directed to Ahrefs' support team. In my experience, such services typically do not disclose details about how they collect and process data. As a result, similar inquiries often go unanswered or receive vague responses.
What tools do you use to analyze competitor brand engagement on social media over a specific period?
I specialize in SEO and don't directly work with social media. However, for cross-channel interaction analysis, such as between SEO and PPC, I can recommend a few approaches. One common example is what's known as "PPC cannibalization," where paid ads start to take away part of the organic traffic — both in categories and at the branded query level.
For analyzing such interactions, I use Similarweb.
Which metric in this analysis is the most reliable? Is it optimal to calculate an average across tools?
For example, Ahrefs shows 86.3k, Semrush shows 133.7k, and Similarweb shows 3.6 million. The Similarweb figure is likely an anomaly. This tool sometimes provides inflated numbers due to its data collection method.
In this case, I would trust Ahrefs more: although it tends to underestimate traffic estimates, its calculations are based on actual data — keywords, their frequency, CTR — everything is factored in. The real numbers, in my opinion, lie somewhere in between Ahrefs and Semrush, around 110k.
Does the margin of error depend on the niche or geography? Is Ahrefs equally accurate in all cases?
Ahrefs consistently provides accurate results regardless of niche or geography. We've analyzed different niches and compared data for different websites — Ahrefs has always been better. Its estimation methodology is conservative: the error margin is usually 30-50% on the lower side, without any sharp deviations.
Similarweb sometimes gives great results with minimal error, but no clear dependency on niche or other factors has been found.
The potential is greater with Similarweb and Semrush, where custom calculation models are used, but for now, Ahrefs’ model works better.
How many keywords in the top 10 and top 3 do you consider when estimating potential traffic?
We always take the most comprehensive keyword set. When calculating potential traffic over a given period, a full range of search queries is needed for detailed analysis.
What results do you get from Serpstat and SE Ranking?
I can't provide a well-grounded evaluation of SE Ranking. However, I believe Serpstat is on par with Ahrefs. In some cases, its keyword database even performs better. I expect Serpstat to have a similar margin of error as Ahrefs.
We thank Vladyslav for such an informative case study and wish him, and you, all the best in your future SEO endeavors.
If you’re looking for more insights and SEO tips, be sure to check out our Collaborator's podcast, where we dive deeper into industry trends, and connect with us on LinkedIn for ongoing discussions and updates!
Related reading
- • How to Check Backlinks to a Website. Tools for Testing and Analysis of Backlinks
- • Step-by-step Case on How to Get a Link to a Site for Free
- • Why They Love Ahrefs: An Overview of the Service's Capabilities
- • Collaborator + Serpstat: Official Integration
- • JavaScript SEO – How to Optimize SPA Sites for Search Engines and AI