Grounding in AI is when a model, such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, or Google’s AI Overviews, checks real, up-to-date information from the web instead of relying only on what it learned during training.
Not every query requires grounding, but when it does, AI models generate answers based on authoritative and current sources. And, believe it or not, these grounded answers can be influenced by a little bit fine-tuned classic, old-school SEO strategies.
Mark Williams-Cook, a digital marketing director at Candour and founder at AlsoAsked, touched on this topic in his presentation at the Collaborator SEO Conference.
This article explains which queries trigger grounding, how grounding affects SEO, and how keyword research and content strategy actually work in the AI era. No hype or vague “GEO” buzzwords.
Key Takeaways
- Grounding means AI uses live web sources to answer a question, instead of relying only on its training data.
- Only grounded AI answers can be influenced by SEO — non-grounded answers can’t be optimized.
- Grounding usually happens for comparisons, reviews, and recent topics, where up-to-date information is needed.
- When AI is grounded, it runs real search queries similar to Google or Bing searches.
- To influence grounded answers, visibility across trusted web sources matters, not just ranking your own website.
Grounding in AI: How Does it Work?
Grounding in AI occurs when an AI model, such as ChatGPT, Gemini, etc., accesses real, current data from the web rather than from its own training data. Through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), the AI retrieves, digests, and integrates external data into its answers, resulting in grounded, true, up-to-date, and context-aware AI responses.
By concentrating on AI grounding and SEO, your chances of being included in AI-generated answers will increase.
SEO in the AI Age: How to Optimize
Let’s start with comparing traditional engines and AI searches. The first-mentioned followed a simple flow:
User → Google search → List of results
To have their website in that list of results and be visible to its target audience, SEO specialists optimized it for:
- Keywords
- Rankings
- Traffic
- Clicks
The new reality is that millions of users skip search engines for ChatGPT, Claude, or other AI models. AI-driven search adds another layer to the above-mentioned flow, and it looks like this:
User → AI model → Search engine → Web pages → Generated answer
The important part is this:
AI models don’t replace search engines. They depend on them.
When an AI isn’t confident in its own knowledge, it runs real searches in the background. Those searches still rely on Google or Bing indexes. And this is what is called “grounding”.
Although the way queries are formed and answers come from has changed:
- Rankings still matter
- Links still matter
- Fresh content still matters
Keyword Research in the AI Era: What Actually Changed and What Didn’t
Traditional keyword research was built around short, exact phrases with measurable search volume. That model struggles today for three reasons:
- Users just talk with AI models instead of searching for something
- AI responses are customized, meaning they adapt to context and personal details
- Intent unfolds across multiple questions, not only one query
Example:
Instead of typing “best vehicles in 2026”, users now say something like:
“I have a family with five kids, and we take short trips every weekend. We also go on summer vacations by car. What budget vehicle should I buy for comfortable long- and short-distance trips, with and without luggage?”
The user doesn’t need to simplify their thinking and surf the web for hours, reading reviews and descriptions. They just describe their needs in detail, and AI does that for them.
Based on that, the job of SEO specialists is no longer to guess what people type. They should understand what searches the AI runs after it understands the user.
That’s why optimization now happens behind the conversation, not just inside the search box.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Optimize for Generative Search
Step 1: Start With Primary Keywords
Despite all the changes AI models brought to SEO, the optimization process still begins with classic SEO inputs:
- The keywords you already track
- The topics you already care about
Think of these as anchors, not final answers.
Let’s take an automotive topic, for example, as we have already mentioned. So these are primary keywords you can take:
- family vehicles
- best family vehicles
- best family vehicles in 2026
On their own, they’re too broad and just give you a base to work from.
Step 2: Build Personas and Person-Focused Keywords
Knowing your target audience, its needs, preferences, and problems is more important than ever before, as AI answers depend on who’s asking.
A parent of five kids leading an active traveling life won’t get the same advice as a single city driver. The one looking for a budget vehicle doesn’t care about leather interiors or chrome trims.
That is why don’t try to optimize for “everyone” but define a few realistic user profiles:
- experience level
- goals
- limitations
- values
As an example:
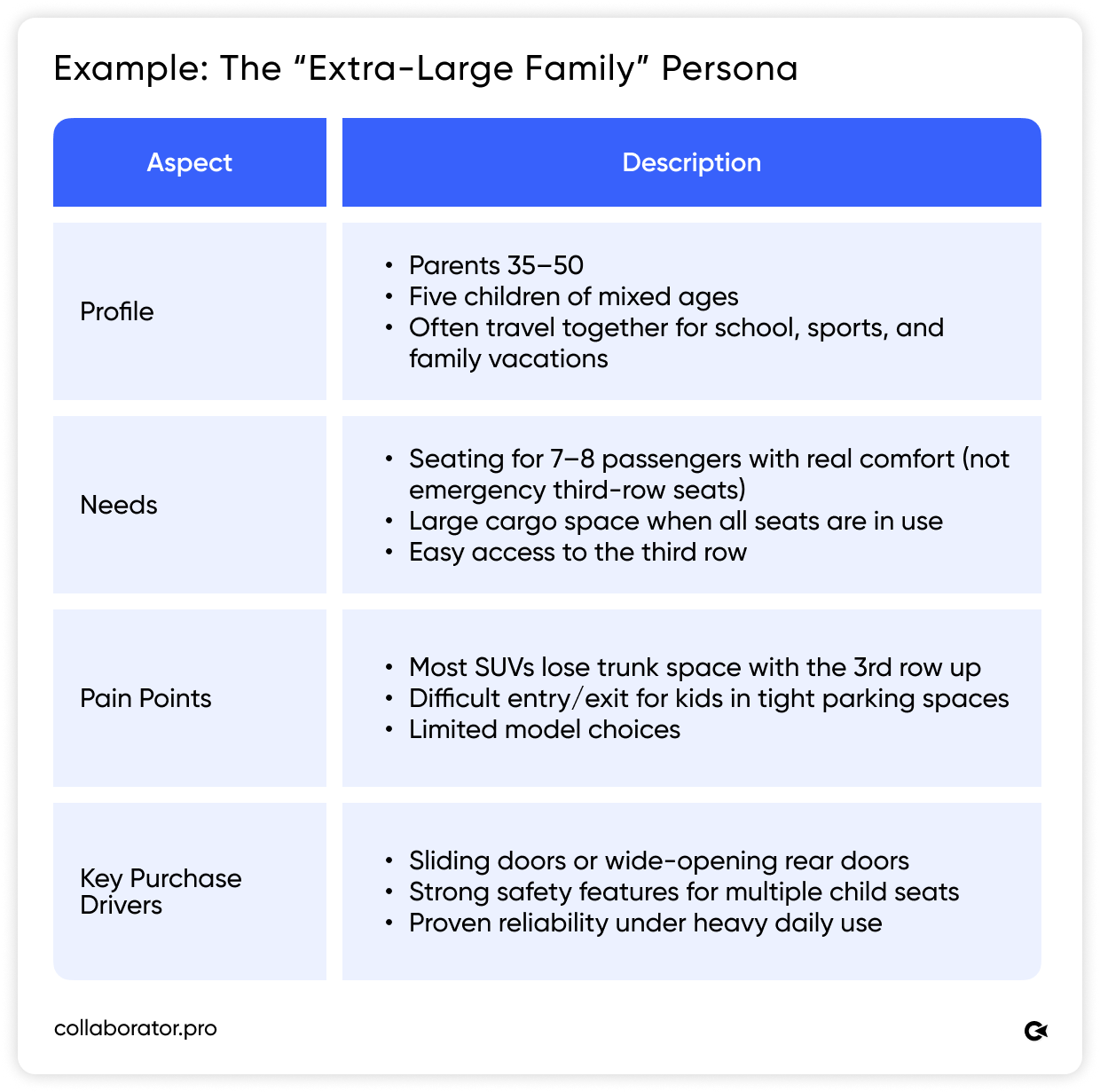
Then ask an AI to help you rewrite your base keywords from each perspective. We asked ChatGPT to do it for an “extra-large family” persona. Its answer is in the screenshot below.
One keyword can turn into dozens of natural queries.
Step 3: Make a List of the Most Common Questions
Questions people ask in real life and on platforms like Reddit are important to discover, as they are what people actually ask AI models. For instance, a user interested in an affordable vehicle for a big family most probably asks the following questions:
- Which vehicles can comfortably seat 7–8 passengers?
- What are the best minivans for large families?
- Which full-size SUVs have a spacious third row?
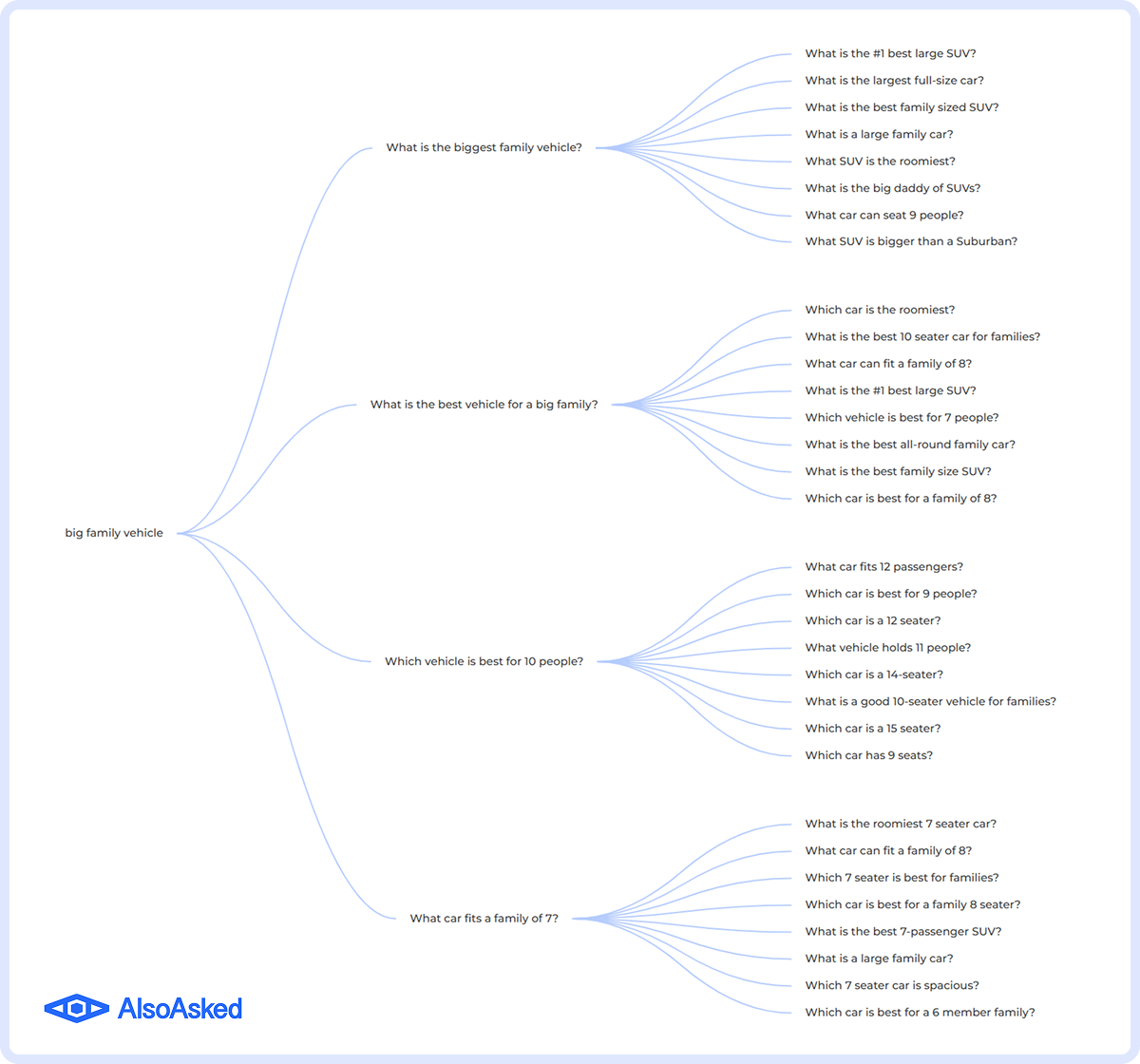
To streamline the process of making a list of frequently asked questions, you can use the People Also Asked (PAA) tool. It allows you to target your search for a specific country, city, language, and even search depth. We’ve used it for a query “big family vehicle”.
As you can see, it generates common questions and what users tend to ask next. This is incredibly valuable because it reveals how intent develops over time, not just in one search.
Step 4: Find Out Potential Prompts
You can use any AI model to make a list of potential prompts, providing it with your base keywords, personas, and PAA questions.
This way, you can easily get thousands of potential prompts. That sounds impressive, right? However, most of them don’t matter, and the key isn’t volume. It’s knowing which questions AI answers using the web.
Step 5: Classify Grounded vs. Non-Grounded Answers
This is where most people get AI SEO wrong.
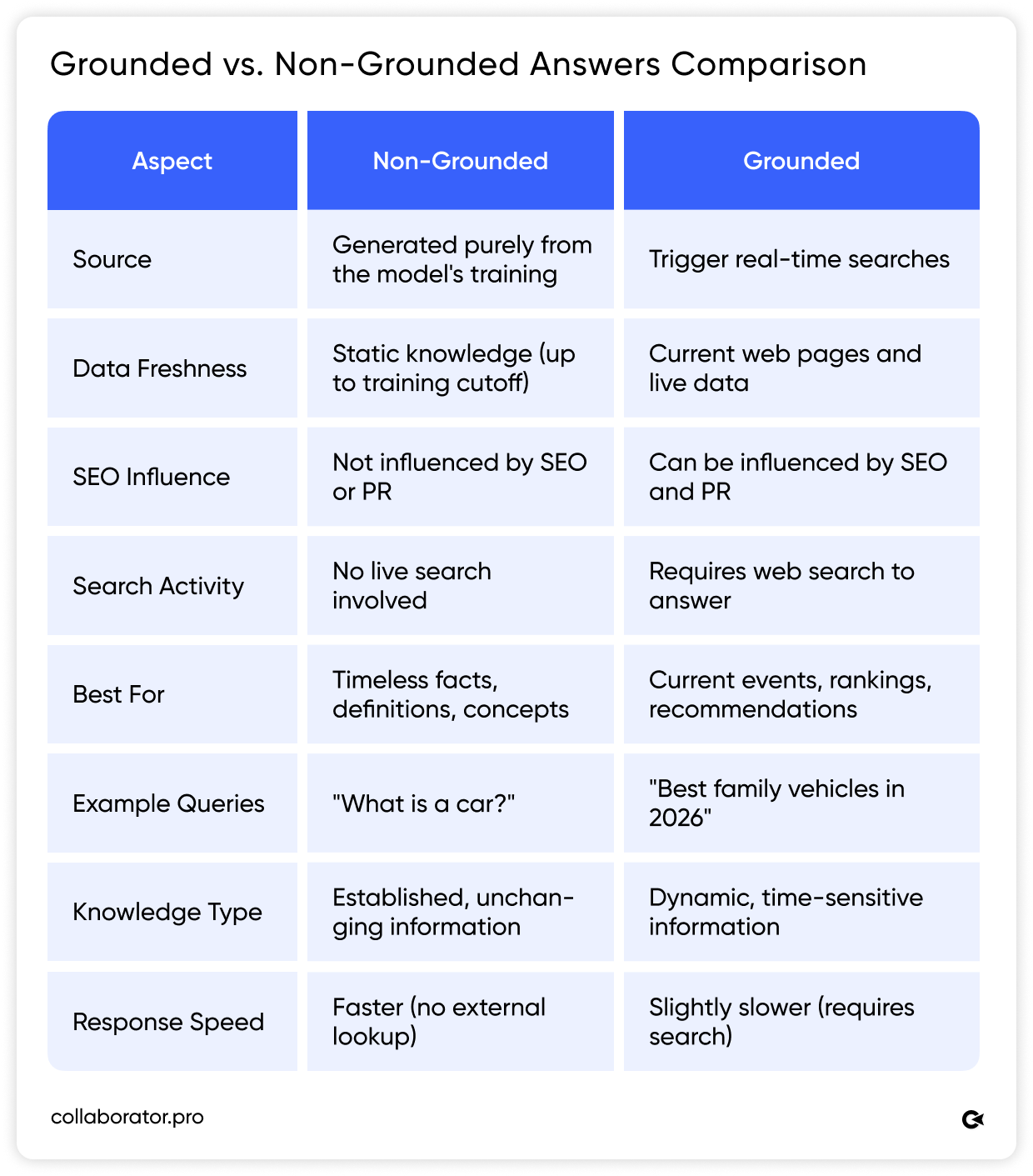
As we have mentioned above, there are two types of AI answers: grounded and non-grounded. To quickly understand the difference between them, see the comparison table below:
If a question isn’t grounded, optimizing for it is a waste of time.
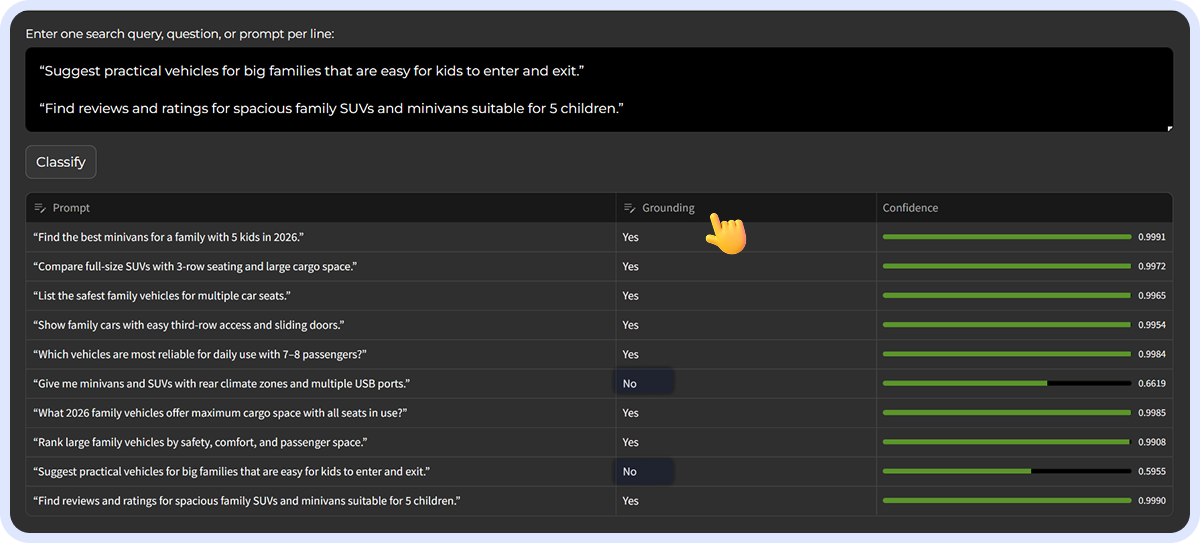
You can use QDG Classifier, built by Dejan AI, to quickly filter out non-grounded questions in your list of keywords and FAQs and clearly see where your time and effort will have the greatest impact.
Simply paste your list into the window, click the “Classify” button, and you’ll immediately see which queries are grounded and which aren’t.
Final Thoughts
AI models don’t immediately know the answer to any question. Some prompts make them search for external information on the web.
These background searches are very similar to regular Google ones, and in many cases, you can influence them by using slightly improved, well-known SEO tricks.
Here is where AI optimization loops back to traditional SEO:
- You find the real queries
- You see what ranks
- You optimize for those results
Same game. Different entry point.
Related reading
- • Do Backlinks Work for AI Assistants and AI Overviews?
- • JavaScript SEO – How to Optimize SPA Sites for Search Engines and AI
- • Google AI Overviews (AIO) in Collaborator: a New Metric for Effective Link Building
- • How to Use ChatGPT for Link Building: 10+ Best Techniques You Should Try
- • ChatGPT for SEO: 17 Best Use Cases and Examples