Toxic Backlinks: How to Find and Remove Harmful Links

Links play a major role in a successful, sustainable SEO strategy.
But not all links are equal. While good quality links can enhance your rankings and build authority, toxic or “bad” backlinks may harm your website’s SEO.
Toxic backlinks are risky because link quality reflects your site’s authority and relevance — key factors Google values in its search rankings. Given the potential for these bad backlinks to impact your website’s rankings, it's essential to monitor them regularly to maintain a healthy backlink profile.
To help minimize the impact of toxic backlinks, we’ve outlined everything you need to know about identifying and removing them for long-term SEO success.
Ready to take out your website’s trash?
What Are Toxic Backlinks?
Toxic backlinks are low-quality or harmful inbound links from unreliable, spammy, or irrelevant websites. Search engines generally view them as red flags that can lead to penalties and harm your site’s SEO, reducing visibility and credibility. These bad backlinks can come from a variety of low-quality sources, including:
- Paid link schemes
- Private blog networks (PBNs)
- Blog forums
- Link farms
- Sites with excessive ads
- Unrelated content
- Penalized domains
- Automated link-building tools
Because they often exist solely to manipulate search engine rankings by linking to a high domain authority (DA) domain, bad backlinks generally have little to no relevance to the audience of the site they’re posted on. For example, a cannabis ecommerce store or casino affiliate site may link to a SaaS site like Salesforce or MailChimp that has a high DA but little to no potential crossover audience. This makes them look like spam backlinks to search engines, as there is no real reason or relevance for them to be included on the site.
In contrast, high-quality backlinks are essential for building trust and authority. When reputable websites link to your content, search engines interpret this as a positive trust signal, affirming your site’s relevance and value. These “good” backlinks indicate to search engines that other credible sites find your content useful, which can boost your rankings, attract organic traffic, and improve online authority.
Despite being a common term used by numerous SEO tools, Google doesn't officially call bad backlinks “toxic backlinks.” However, it does classify them as “link spam” under its spam policies. But in the SEO community, there's a clear distinction between toxic, spammy, and manipulative backlinks:
- Toxic backlinks are links from untrustworthy sites that harm a website’s credibility and can lead to penalties. These links often come from low-quality, penalized, or malicious sites.
- Spammy backlinks usually involve excessive, low-quality links from irrelevant sources, link farms, or automated bots, aiming to boost rankings without regard for content relevance.
- Manipulative backlinks are deliberately designed to trick search engines into boosting a site’s ranking. These might include hidden links, paid links without disclosure, or excessive anchor text manipulation.
While all three types can harm your site’s SEO, understanding their differences helps you to check spam backlinks for potential threats, prioritize their removal efforts, and maintain a healthier link profile.
19 Red Flags of Bad Backlinks
Your backlinks act as votes of confidence from other websites, signaling to search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy. However, not all backlinks are created equal. Some can do more harm than good, dragging down your website's ranking and reputation. That's why understanding what makes a backlink "bad" is crucial for any website owner or digital marketer looking to climb the search engine ladder.
Here are 19 red flags that scream "bad backlink!". By identifying and avoiding these, you can ensure that your link-building efforts contribute positively to your SEO strategy and help you reach your digital marketing goals.
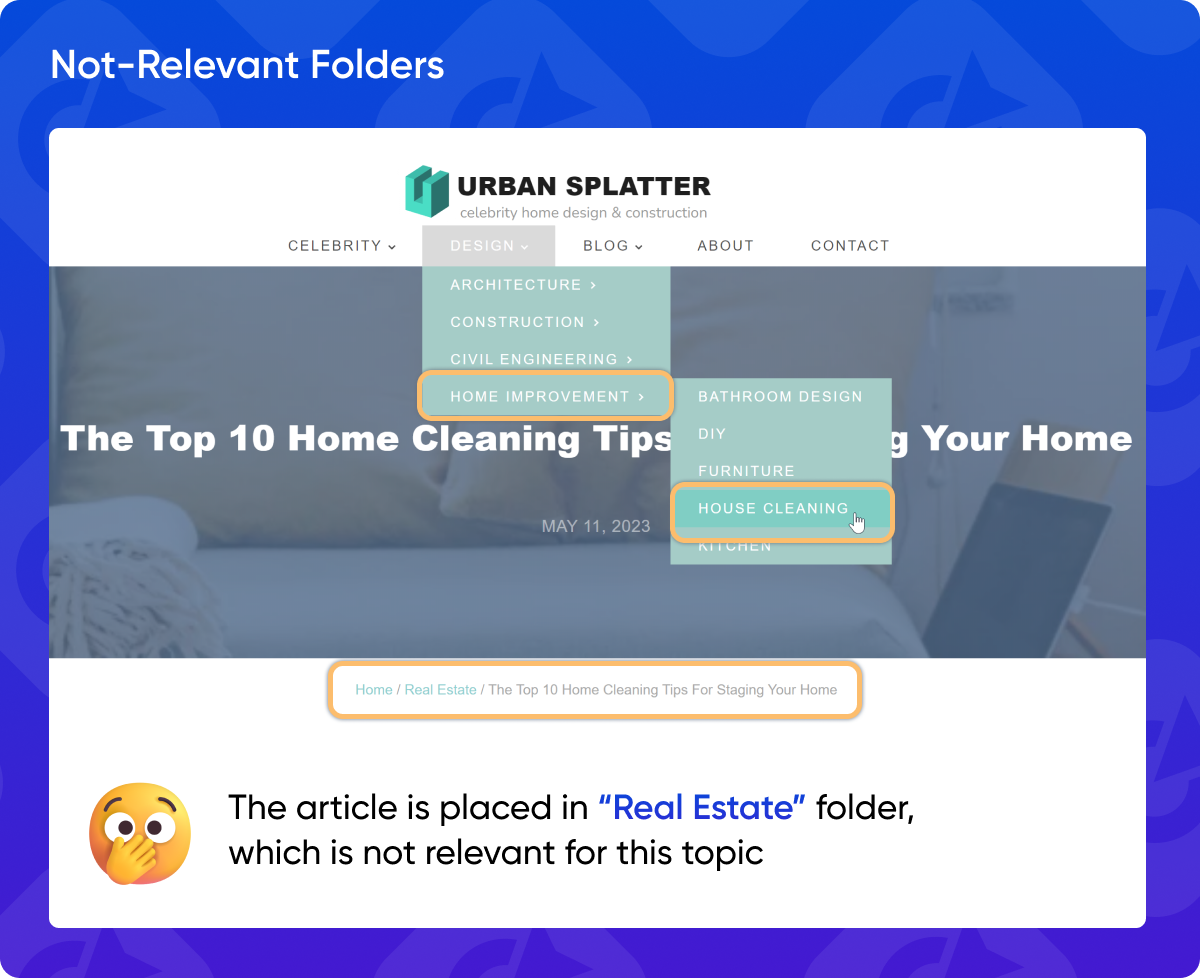
1. Not Relevant Folders
A backlink from a website completely unrelated to your niche is unlikely to be valuable. For instance, a link from a pet grooming website to your blog about cryptocurrency will seem out of place and suspicious to search engines. Always aim for backlinks from websites within your industry or those covering related topics. This ensures that the link makes sense in context and adds real value for users navigating the web.
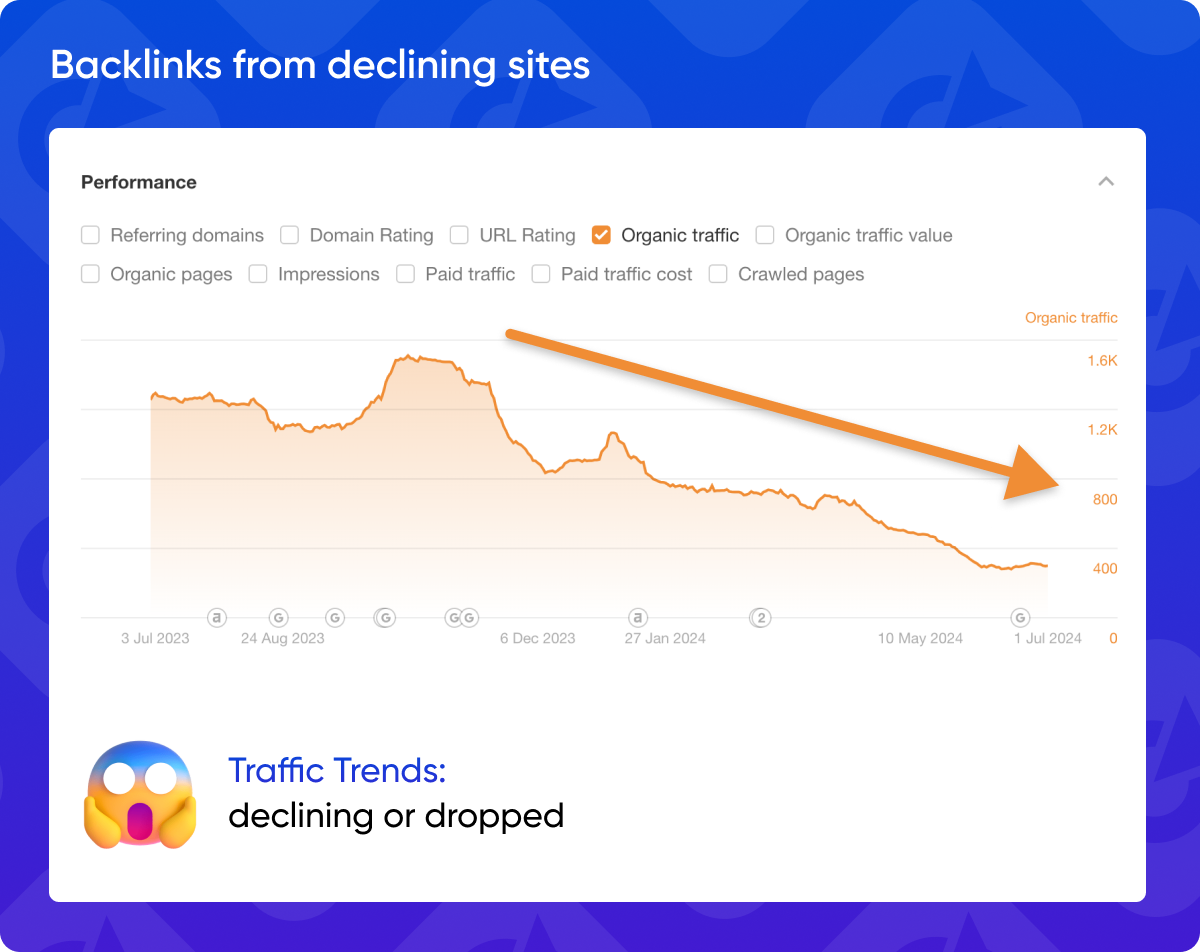
2. Backlinks from declining sites
Backlinks from websites with declining traffic and engagement can negatively impact your SEO. Monitor the traffic trends of the linking website to ensure it's still relevant and authoritative.
3. Lack of Relevant Keywords
If the linking website doesn’t rank for relevant keywords in your industry, the backlink may not be as valuable. Look for websites that demonstrate topical authority and relevance to your niche.
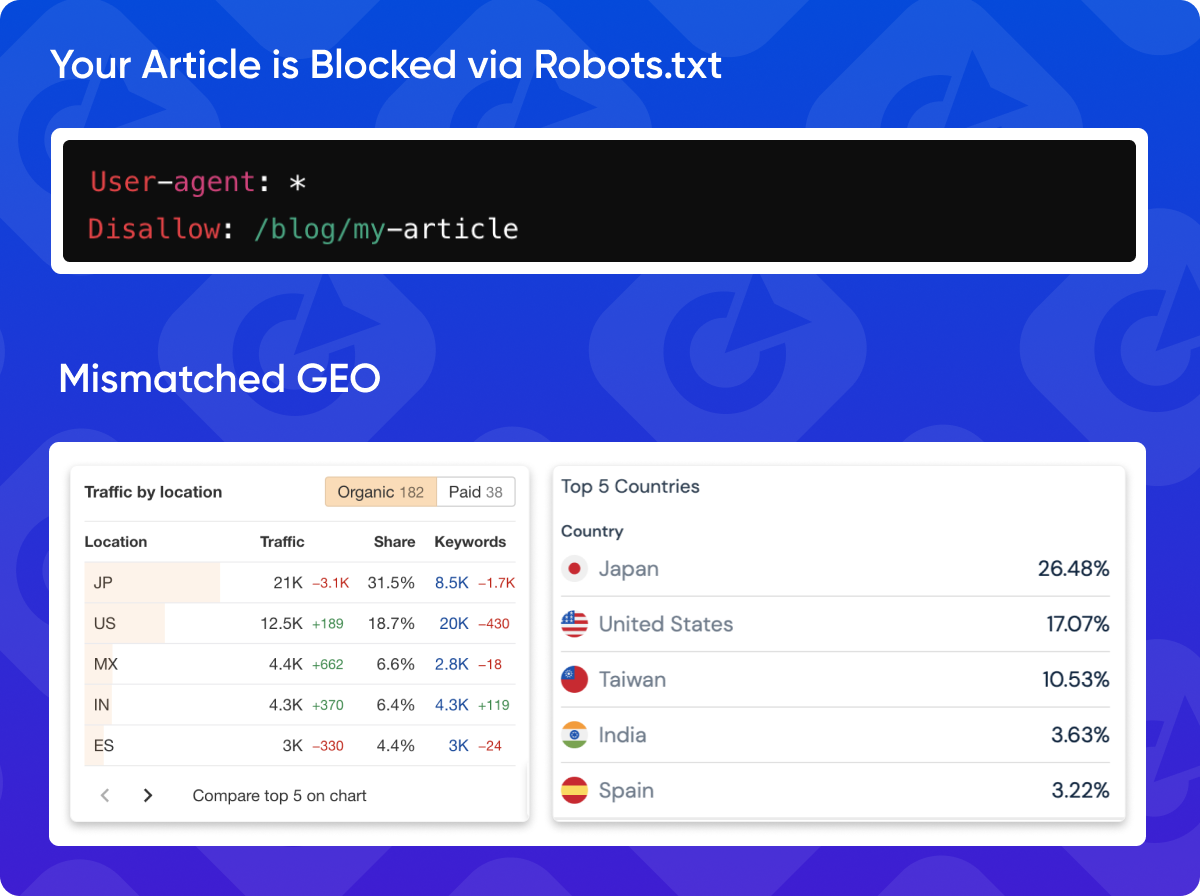
4. Mismatched GEO or Your Article is blocked via Robots.txt
Backlinks from websites targeting a different geographical region than your target audience may not be as valuable. Aim for backlinks from websites that align with your target market.
If a website blocks search engines from accessing certain pages or sections through its robots.txt file, any backlinks from those blocked areas are essentially useless.
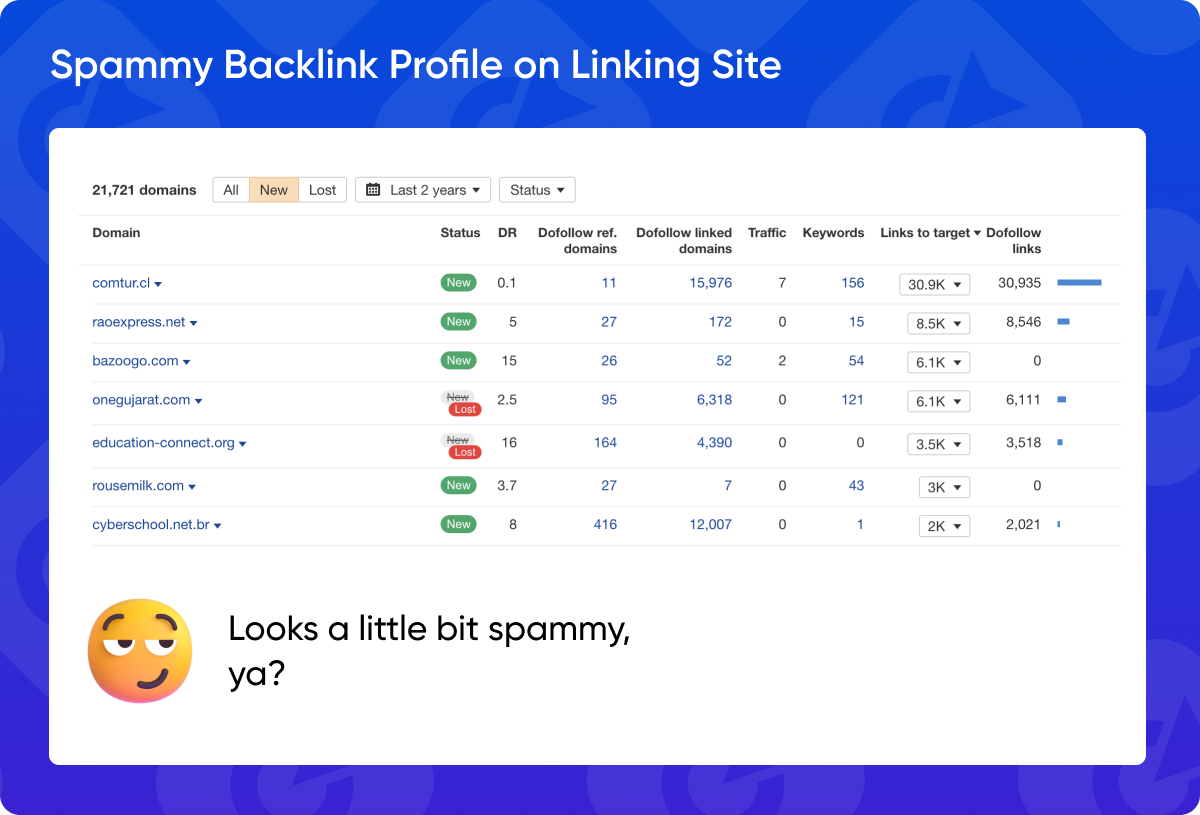
5. Spammy Backlink Profile on Linking Site
A website with a high number of spammy or low-quality backlinks of its own can negatively impact your website’s SEO. Analyze the backlink profile of the linking website to ensure it’s reputable.
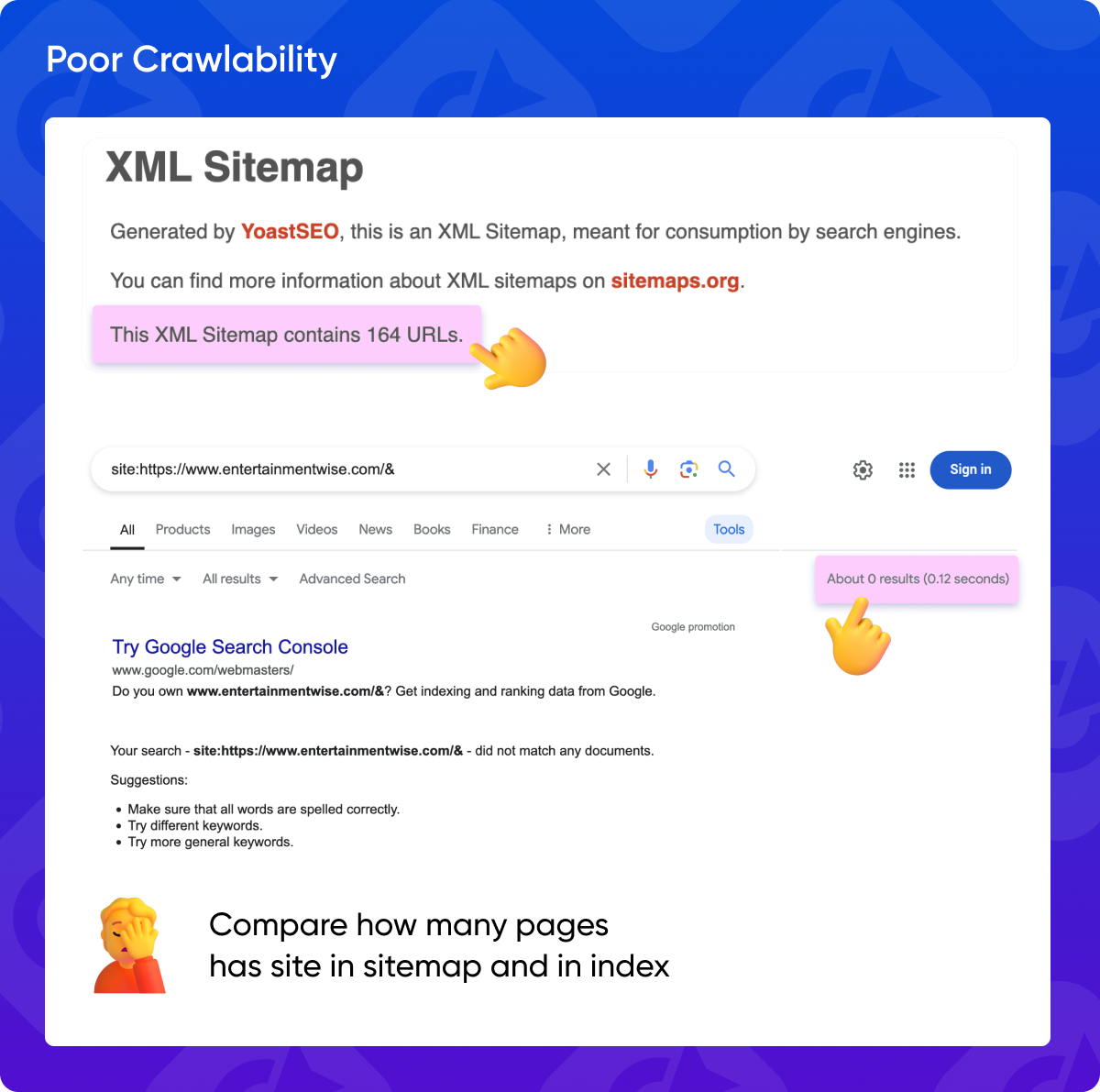
6. Poor Crawlability
Search engines need to be able to easily crawl and index the linking website for your backlink to be effective. Check the sitemap and compare it to the number of pages indexed to assess crawlability.
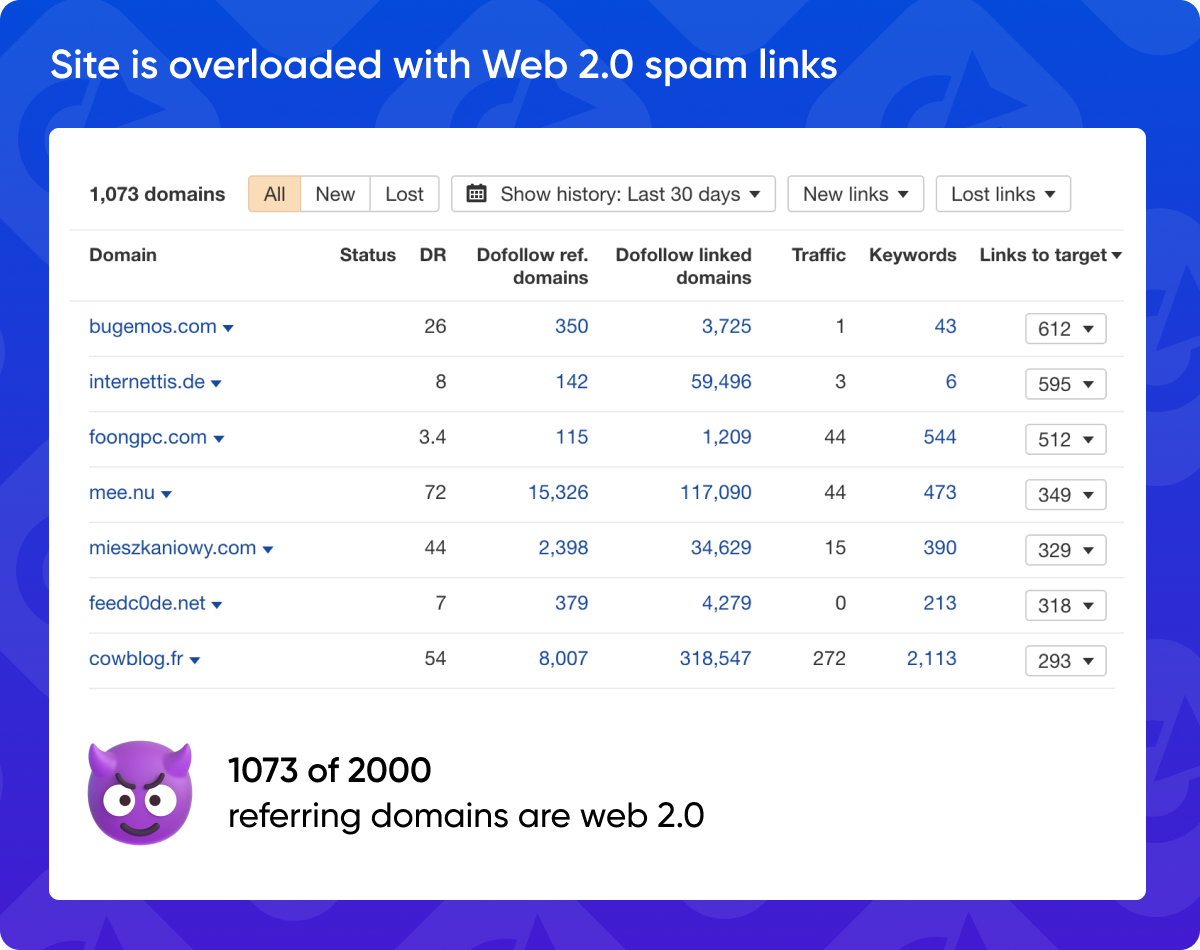
7. Site is overloaded with Web 2.0 spam links
An excessive number of backlinks from Web 2.0 platforms, especially those with low domain authority or spammy content, can be detrimental to your SEO efforts. Focus on obtaining backlinks from reputable and relevant websites.
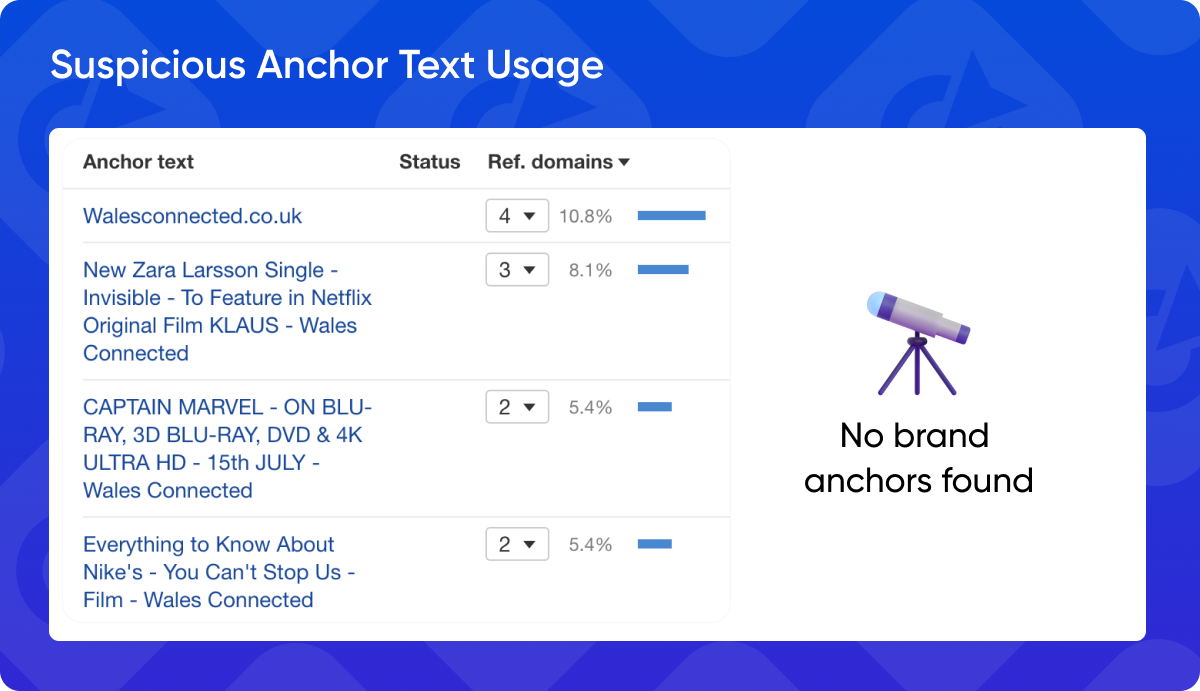
8. Suspicious Anchor Text Usage
Anchor text is the clickable text of a hyperlink. Avoid backlinks with keyword-stuffed or irrelevant anchor text. Aim for natural and descriptive anchor text that accurately reflects the content it links to.
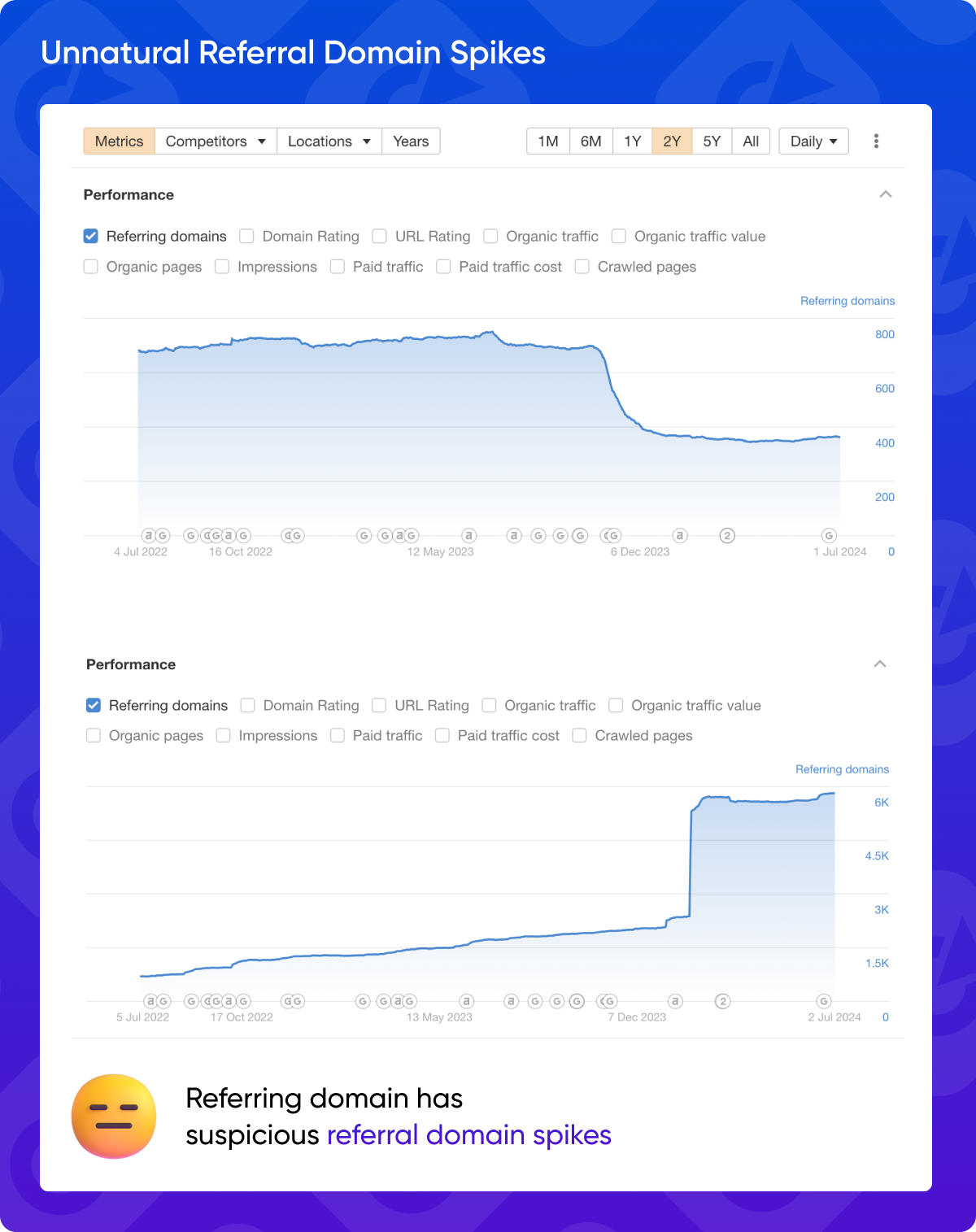
9. Unnatural Referral Domain Spikes
A sudden and unexplained spike in referring domains to the linking website can be a sign of suspicious activity. Investigate any unusual patterns in referral traffic.
10. Low-Quality Content
Backlinks from websites with low-quality, auto-generated, or spammy content can damage your website’s reputation and SEO. Aim for backlinks from websites that provide high-quality, valuable content.
To detect AI-generated content, you even don’t need any special tools. If you see a text containing many of the following words, it’s most likely generated by an AI tool.
|
1. Delve |
26. Paradigm |
51. Elucidate |
|
2. Harnessing |
27. Dynamics |
52. Substantiate |
|
3. At the heart of |
28. Implications |
53. Resonate |
|
4. In essence |
29. Prerequisite |
54. Catalyze |
|
5. Facilitating |
30. Fusion |
55. Resilience |
|
6. Intrinsic |
31. Holistic |
56. Evoke |
|
7. Integral |
32. Quintessential |
57. Pinnacle |
|
8. Core |
33. Cohesion |
58. Evolve |
|
9. Facet |
34. Symbiosis |
59. Digital Bazaar |
|
10. Nuance |
35. Integration |
60. Tapestry |
|
11. Culmination |
36. Encompass |
61. Leverage |
|
12. Manifestation |
37. Unveil |
62. Centerpiece |
|
13. Inherent |
38. Unravel |
63. Subtlety |
|
14. Confluence |
39. Emanate |
64. Immanent |
|
15. Underlying |
40. Illuminate |
65. Exemplify |
|
16. Intricacies |
41. Reverberate |
66. Blend |
|
17. Epitomize |
42. Augment |
67. Comprehensive |
|
18. Embodiment |
43. Infuse |
68. Archetypal |
|
19. Iteration |
44. Extrapolate |
69. Unity |
|
20. Synthesize |
45. Embody |
70. Harmony |
|
21. Amplify |
46. Unify |
71. Conceptualize |
|
22. Impetus |
47. Inflection |
72. Reinforce |
|
23. Catalyst |
48. Instigate |
73. Mosaic |
|
24. Synergy |
49. Embark |
74. Catering |
|
25. Cohesive |
50. Envisage |
Even without tools! |
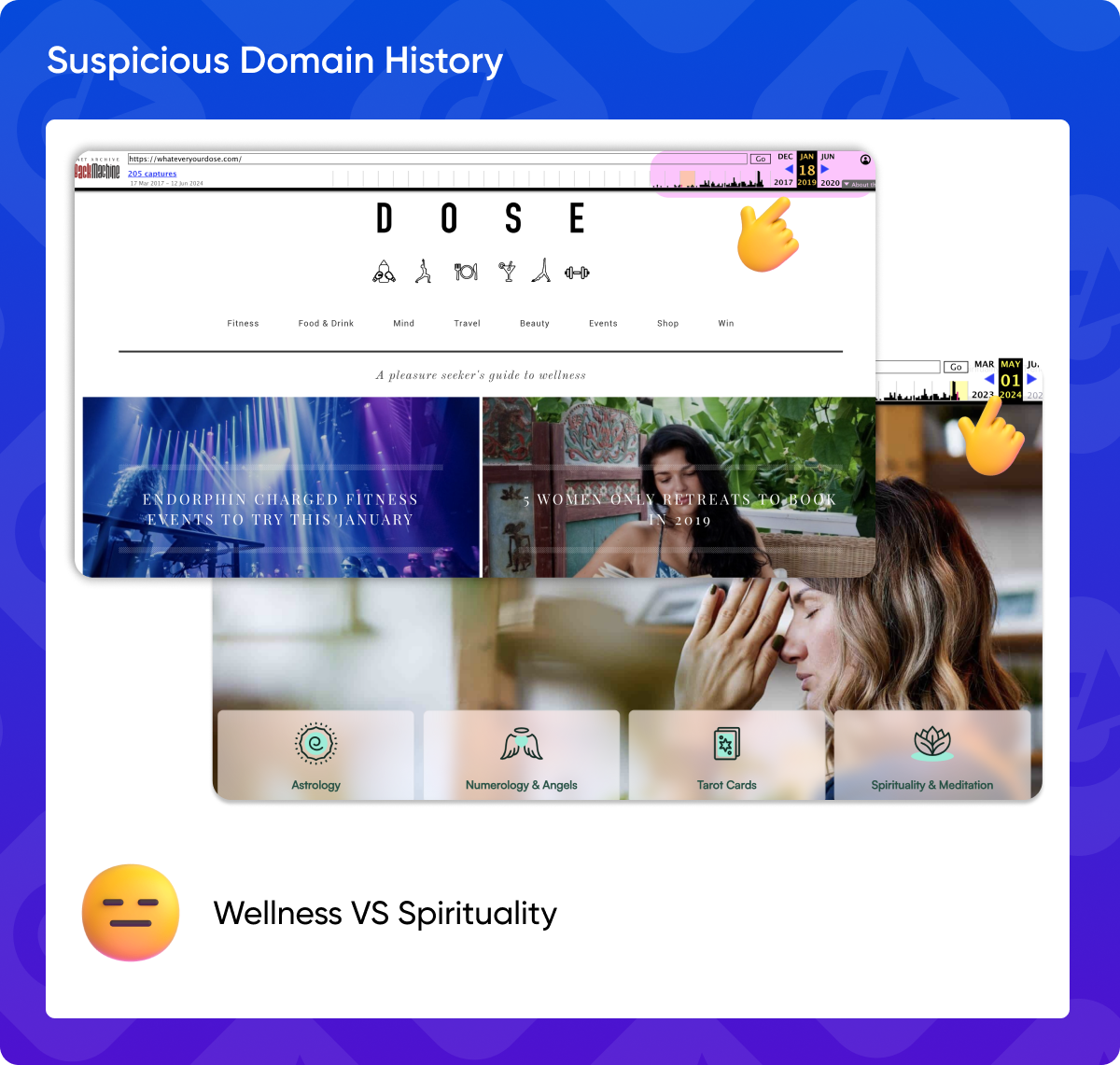
11. Suspicious Domain history
Websites with a history of changing domains or inconsistent content can raise red flags. Carefully examine the history of the linking website to ensure it’s legitimate and trustworthy.
12. Links from Pages with Issues
Backlinks from pages with technical issues, such as "noindex" meta tags, non-canonical URLs, or broken links, can harm your SEO. Carefully inspect the linking page for any potential problems.
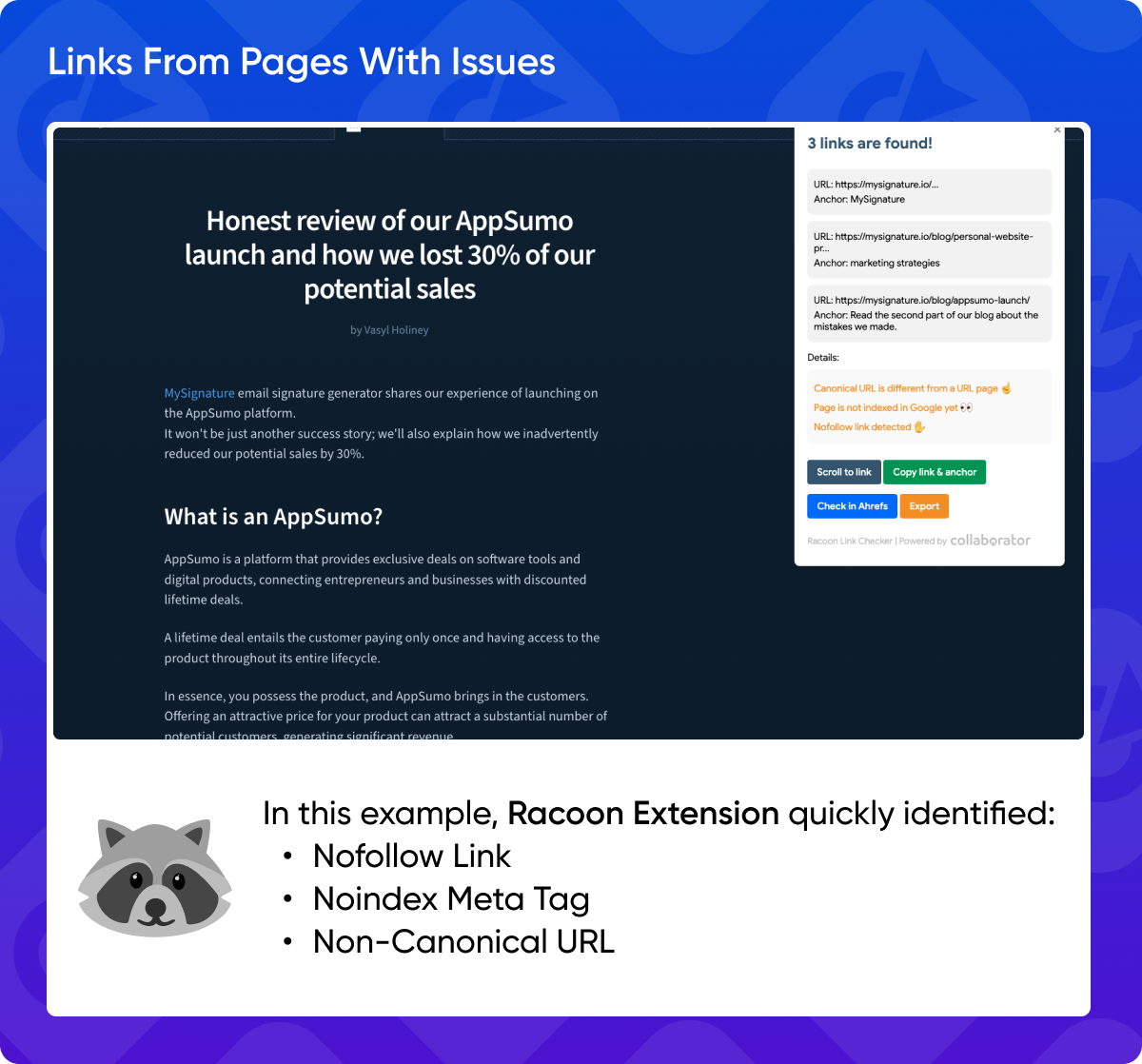
To save time and effort, you can use Racoon, a free Chrome extension developed to simplify and speed up the link-checking process. All you need to do is download it and specify which domains it should search for. The next time you visit the linking page, Racoon will instantly find your links and display their attributes.
Try Racoon Link Checker
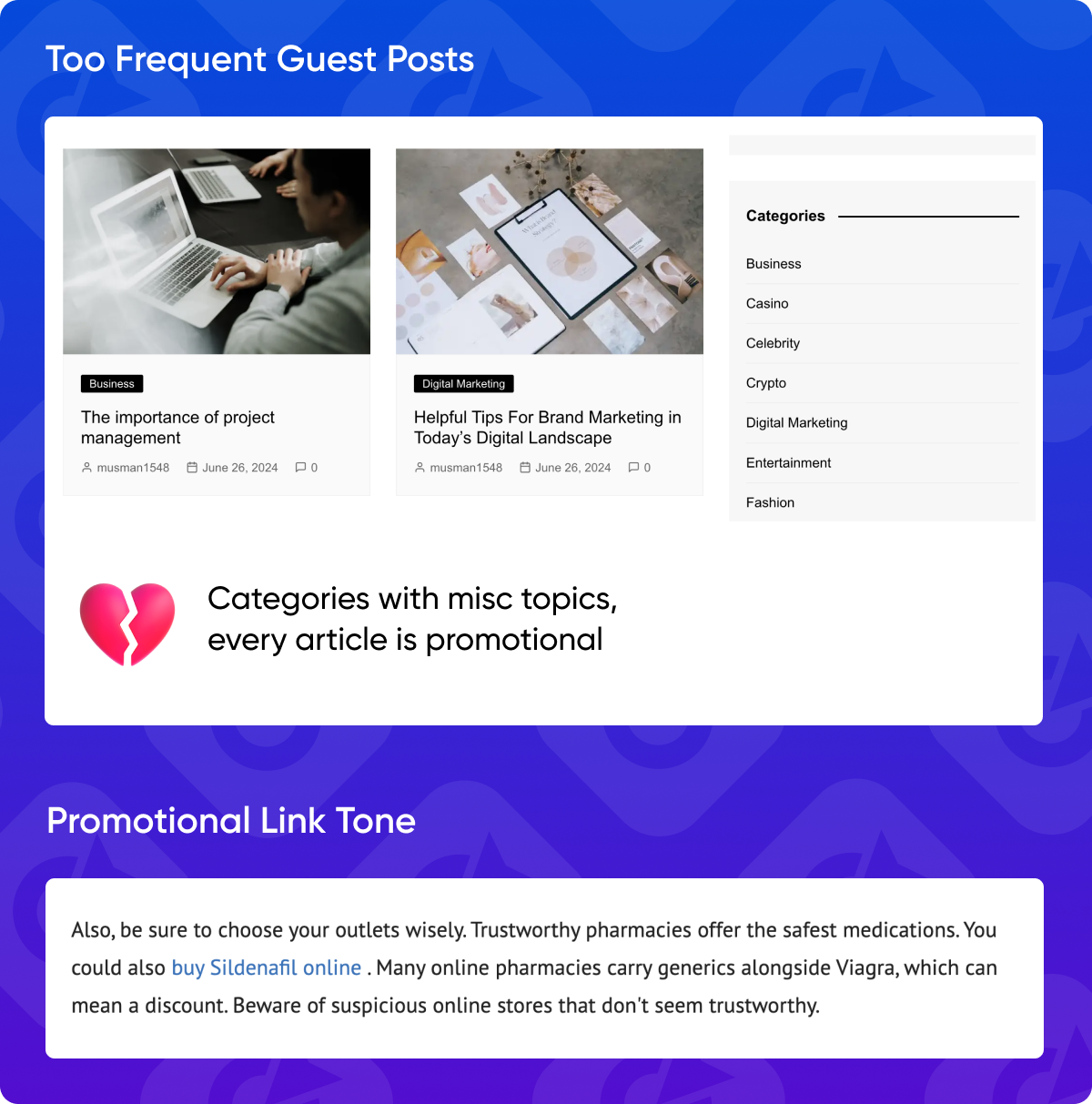
13. Too Frequent Guest Posts & Promotional Link Tone
While paid or free guest posting can be a valuable strategy, excessive guest blogging on the same website can appear manipulative and raise red flags with search engines.
Backlinks should appear natural and provide value to users. Overly promotional or salesy anchor text and surrounding content can signal a low-quality backlink.
14. No Author Expertise
Backlinks from authoritative sources in your niche carry more weight. If the author of the linking content lacks expertise or credibility, the backlink may hold less value.
15. Bad Content Formatting
Poorly formatted content on the linking page can reflect negatively on your website. Ensure the linking page is well-structured, easy to read, and adheres to best practices for online readability.
16. Orphaned Pages
Orphaned pages are pages that are not linked to from any other page on the website. Backlinks from orphaned pages are less valuable because they are not easily discoverable by search engines.
Tip: If you have such pages on your website, follow the advice given by Emily Gertenbach in one of Collaborator’s podcasts and link them to high-performing URLs.
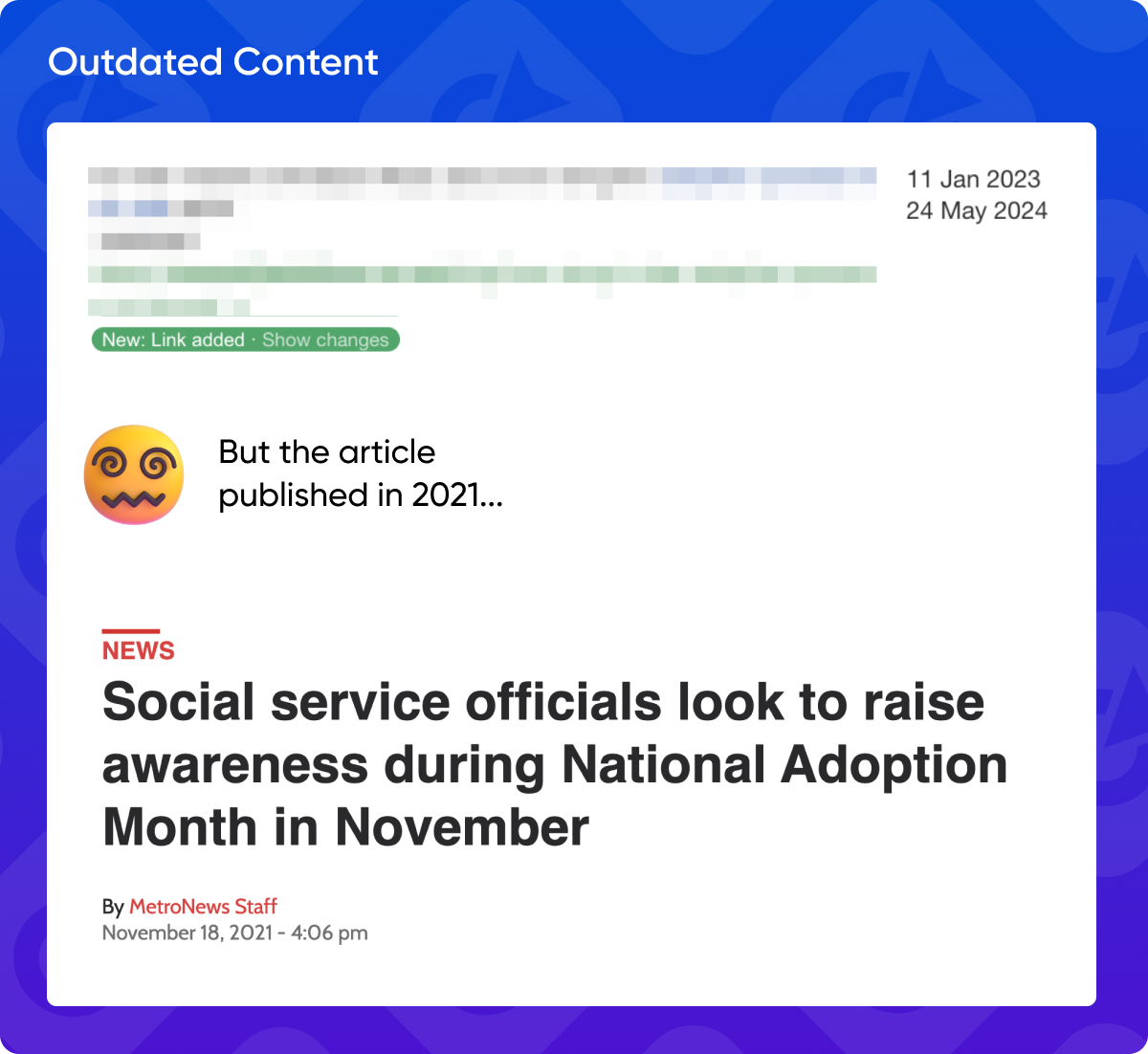
17. Outdated Content
While evergreen content can remain relevant over time, backlinks from outdated articles may not be as valuable. Ensure the linking content is up-to-date and provides current information.
How Toxic Backlinks Affect SEO and Rankings
Understanding how toxic backlinks impact SEO and learning to identify and manage them is essential for building a strong, sustainable web presence. In SEO, credibility is key, and these bad backlinks can severely damage your website’s performance by signaling to search engines that your site is connected to low-quality or manipulative practices that are intended to boost your rankings.
As search engines aim to deliver the most relevant and reliable content to users, this goes against their spam backlink guidelines. This means that a website with a high volume of toxic backlinks is perceived as untrustworthy, so search engines may lower its organic visibility to protect the overall user experience. This means that your site will slip down the Google rankings, and you’ll end up a few spots or a few pages from where you ranked previously.
Even a small slip in rankings can have a major effect on your business or brand. Studies show that only 0.63% of people click through to the second page of Google search results, while those in the top-ranking organic spots are ten times more likely to be clicked on than the search result in the tenth spot. Additionally, if you can improve your ranking by a single spot, your click-through rates can also improve as much as 2.8%.
Despite the potential for a drop in rankings, Google’s John Mueller says that:

However, while Google knows that you have no control over their appearance, a pattern of toxic links may still trigger penalties that can have a massive ripple effect on your SEO.
These bad backlinks penalties can occur in two ways: through algorithmic actions or manual actions.
Algorithmic penalty
Algorithmic Penalties Overview: Google automatically applies penalties for spam policy violations using SpamBrain. The search engine launched this AI-powered system in 2021, and it has been extremely effective in identifying spam sites. When an algorithmic penalty is applied, it can lower a site’s rankings and visibility without notifying the website owner. This means that your site can suddenly be penalized without you realizing why, making it far harder to recover traction in the SERPs (search engine results pages) and regain your spot.
SpamBrain and Updates: SpamBrain was designed to be a robust, ever-evolving platform that focuses on all types of abuse, including detecting practices like link buying and spammy links. As spam tactics change all the time, Google continuously improves and updates its performance to ensure it can effectively identify new forms of spam as they arise.
Manual Review Support: To double up on efficiency, Google’s human reviewers assist SpamBrain by spotting spam that algorithms may miss, adding an extra layer of detection. Users can also provide feedback about searches on the search results page, maintaining the human-to-human connection. This feedback may identify bad backlinks that are otherwise missed, or it may confirm to Google that a site is untrustworthy or using bad backlinks to manipulate its position in the SERPs.
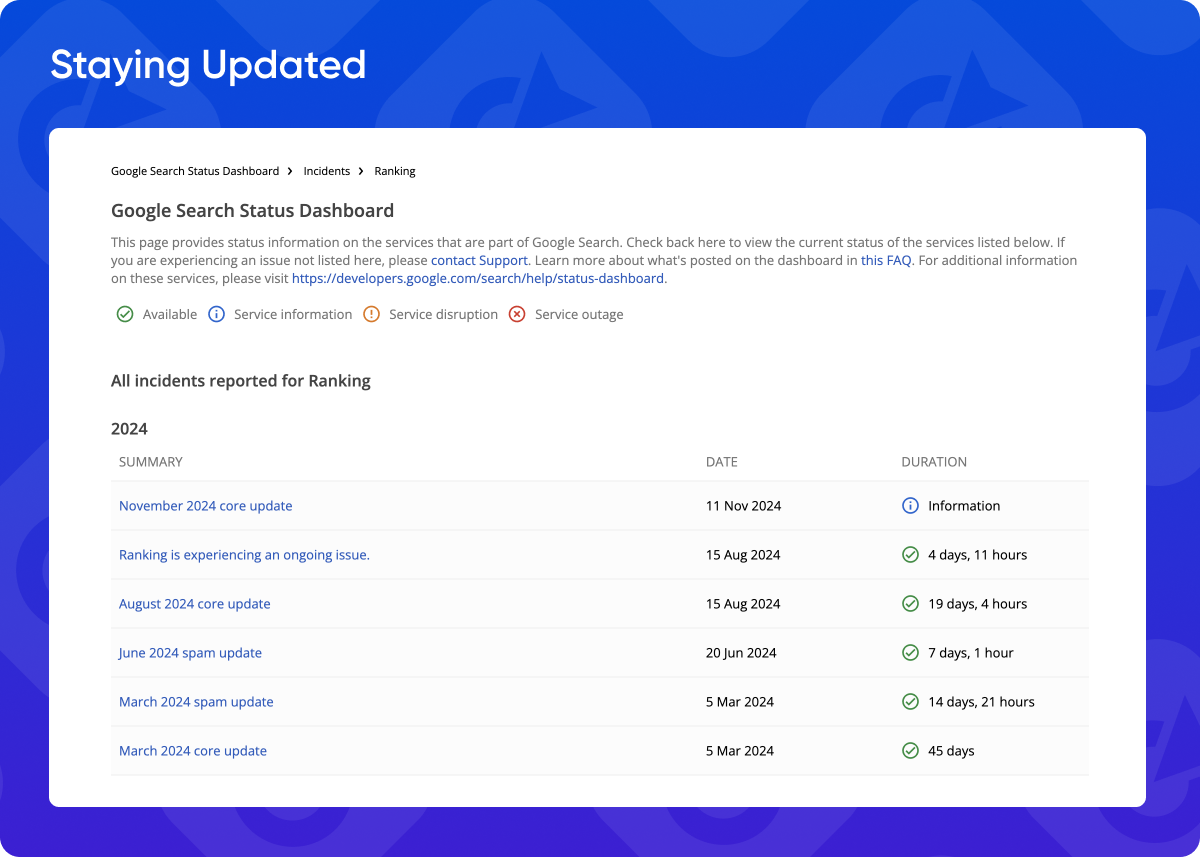
Staying Updated: To stay ahead of evolving spam detection practices and avoid penalties, you need to monitor Google’s updates and guidelines regularly. Google’s Search Status Dashboard makes it easy to keep track of changes as they happen and to adjust your SEO strategy as needed. However, it’s also a good idea to follow industry news, engage with other members in SEO forums, and seek insights from SEO experts to understand the implications of new updates. By regularly reviewing your site’s link profile, you can help to ensure it remains aligned with best practices, reducing the risk of future penalties.
Manual action
Role of Google’s Review Team: The human evaluators that assist SpamBrain manually assess websites to identify potential violations of Google’s spam policies. This includes examining sites for toxic backlink profiles—collections of low-quality, manipulative links meant to boost rankings artificially. When the team detects these activities, they may issue a manual action to prevent the site from unfairly benefiting in search results, helping to maintain the integrity of Google’s search ecosystem.
Receiving and Responding to Manual Penalties: Unlike with an algorithmic penalty, when your website receives a manual penalty, Google notifies the site owner through their Search Console. The notification includes details on the violation type so you can better understand the issue. To recover from a manual penalty, you must address the problem by removing or disavowing toxic backlinks and then submit a reconsideration request demonstrating the corrective steps you took to regain Google’s trust.
The Rarity of Manual Actions: Google now relies heavily on algorithmic systems like SpamBrain to detect and address spam issues automatically, making manual penalties less common. Most of the traffic drops we see today are due to these algorithmic changes, not manual penalties. As a result, site owners rarely receive direct notifications, making it essential to monitor traffic patterns and adhere to Google’s guidelines to avoid unexpected drops.
Overall, both algorithmic and manual penalties can result in a decline in organic rankings, which limits your visibility in the SERPs and reduces website traffic. Beyond direct penalties, even if Google ignores toxic links or considers a percentage of them as normal, they still dilute your site’s backlink profile, making it harder for quality signals to stand out.
Tools for Detecting Toxic Backlinks
Knowing how to find bad backlinks is an essential part of any SEO strategy. Popular SEO tools like Ahrefs and LinkResearchTools are both great options if you want to check spammy backlinks, as they can perform backlink audits. These audits help you to find toxic backlinks and monitor and manage link quality to prevent penalties.
In Ahrefs, you can use the Backlink Checker to see the strength and quality of each link, filtering for factors like domain authority, and relevance.
LinkResearchTools has a Backlink Profiler to assess link quality, flagging potential toxic links based on criteria such as anchor text patterns and link sources. Both of these tools make it easy to check for bad backlinks and to determine whether they have the potential to impact your search engine rankings.
To use these Ahrefs and LinkResearchTools for backlink audits, enter your website URL into the tool's dashboard. The tool will then run a backlink scan to generate a comprehensive report on your site’s link profile, listing all inbound links. This allows you to identify potentially toxic links by evaluating factors such as domain authority, link relevance, and spam indicators. You can do this by looking for patterns, like repeated links from low-quality or unrelated sources, which can signal risk. Once you’ve assessed your link profile, you can decide whether you need to remove bad backlinks or simply keep tabs on them in case they become problematic in the future.
This task shouldn't be a one-and-done, never to be repeated. Bad backlinks can happen at any time, so you should regularly run audits to identify them and analyze their quality indicators. Doing so will help you maintain a clean profile, boost your site’s credibility, and protect against future search penalties.
How To Handle Toxic Backlinks
After identifying toxic backlinks on your website, you need to know how to manage backlinks to avoid any negative SEO repercussions. Fortunately, you can take action in a few different ways.
The first option is actually inaction—you can choose to follow Google’s advice, ignore the bad backlinks, and hope that the search engine’s advanced algorithm and SpamBrain detect and disregard them automatically.
However, if you’re confident that toxic links are the reason you’re experiencing a decrease in search performance and you've ruled out other issues, you can try reaching out to the site owners to request the removal of harmful links. If this approach fails and the problem persists, the next step is to disavow toxic backlinks.
Here’s how to remove bad backlinks from a website in more detail:
Ignore toxic backlinks
If your site’s SEO isn’t experiencing any negative impact, you don’t need to remove bad backlinks. You can make a note of them on your audit and move on. It is, however, a good idea to keep tabs on these links in the future and see if any patterns emerge. If there’s an influx of links from the same site linking back to yours, this is a red flag you shouldn't ignore.
If you're still concerned that Google might consider certain backlinks manipulative, you can take steps to either remove or disavow them.
Contact a site owner to delete the link
In many cases, the easiest way to remove toxic backlinks is by reaching out to the website owner directly. Find their contact details on their site (often in the About Us or Contact Us section or in a contact form format) and send a courteous email explaining why you’d like the link removed.
You can explain that their link is affecting your search rankings because it comes from a low-quality or irrelevant site and that it may affect them in the long run, too. If they don’t respond or decline your request, consider exploring other options, such as disavowing toxic backlinks.
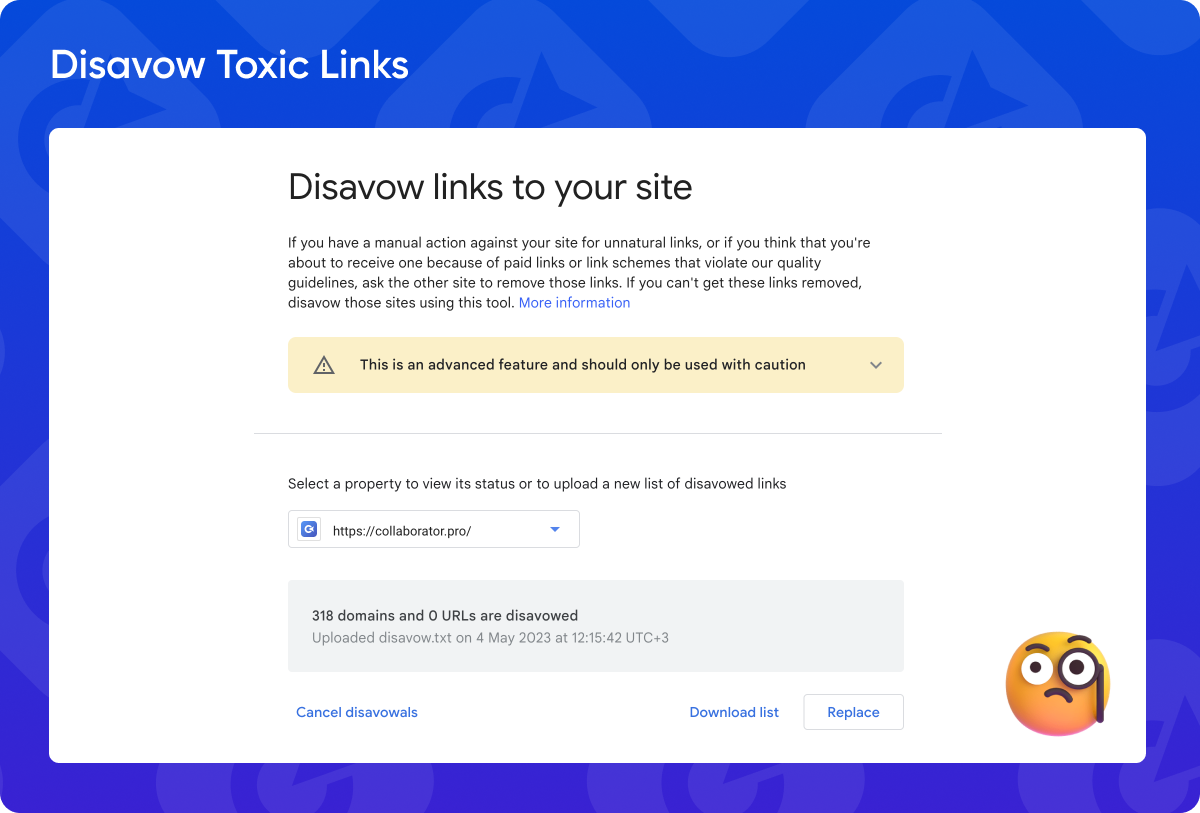
Disavow toxic links
It’s important to note that Google suggests you only disavow toxic links if they have caused or are likely to cause a manual action on your site or if you have a number of artificial, spammy, or low-quality backlinks.
If you want to proceed with disavowing a toxic link, you need to create a text file either manually or using Google Search Console’s Disavow Links. On this page, you must list all the links you want Google to ignore on your site. These links can be individual URLs, or they can be entire domains. If you are regularly getting bad backlinks from a single site, it’s best to disavow the domain in its entirety rather than individual URLs, as the site will likely continue to link back to yours. When you’ve finished creating your disavow file, you’ll submit it to Google Search Console.
Just remember that although you have taken the steps to disavow a bad backlink, there is no guarantee Google will remove it from its index. However, if you know how to disavow toxic backlinks and go ahead with the process, you create a paper trail that tells Google you don’t want that link or domain associated with your website and that you are aware that it can negatively impact your rankings. This paper trail is especially useful if you receive a manual bad backlinks penalty as you have proof that you’ve already taken steps to retain Google’s trust.
Take Action Against Toxic Backlinks & Retain Your Rankings
A quality-focused backlink strategy is crucial to your SEO success as it directly impacts your site’s authority and credibility. By maintaining a clean backlink profile through regular audits using tools from Ahrefs or LinkResearchTools, you can identify and remove toxic backlinks to ensure your website aligns with Google’s standards and retains its rankings.
Having a majority of high quality backlinks signals to search engines that your content is valuable, which helps to strengthen your site’s position in search results. Additionally, regularly reviewing your backlinks keeps your profile adaptable to algorithm updates that emphasize link quality.
By taking a proactive approach to culling bad backlinks and cultivating high quality links instead, you’ll safeguard your rankings and support sustainable SEO growth. Besides, make sure you avoid common SEO mistakes.
Want a healthy backlink profile that helps to maintain your search rankings? Explore our catalog for new guest post opportunities now!